The SAM (Sector Skills Strategy in Additive Manufacturing) project has released the preliminary results of its 3D printing survey, which assessed among other things the role of additive manufacturing education for environmental sustainability.
The EU-funded project is coordinated by the European Welding Federation (EWF), of which 3D Printing Industry is a SAM Associated Partner, and is developing a European Observatory in AM to identify the necessary skills for the technology and deliver them to industry.
As part of this, the project is playing a key role in consolidating the International AM Qualification System (IAMQS), and as a result of the survey’s findings has proposed a new competence unit to address the topic of sustainability within additive manufacturing.

The SAM project
In February, the SAM project published a European Roadmap for Additive Manufacturing with the aim of tackling skill gaps across the sector. The roadmap outlines the critical skills shortage-related challenges currently facing the 3D printing industry and proposes how it intends to address them up to 2030.
Alongside the roadmap, the SAM project also introduced the IAMQS. Supported by a quality assurance system, the IAMQS is comprised of a set of qualifications for different proficiency levels in 3D printing technologies that are aligned with industry requirements and validated by experts.
The IAMQS is deployed through a network of selected training providers with connections to multiple industries that leverage 3D printing. The SAM project has now released a new set of survey results related to additive manufacturing education for sustainability.
SAM’s survey results
The role of education for environmental sustainability is becoming increasingly important, as people throughout Europe face new career challenges across a whole host of different industrial sectors. To adapt to these changes, many workers will need to be re-trained for new skills or expand their existing skill sets, and the need to deliver green, digital and entrepreneurial skills, alongside technical ones, will become more and more crucial in order to show the benefits of implementing sustainable processes in industrial ecosystems.
While environment and climate goals appear to be regarded with high importance by the European Commission and United Nations’ policy agendas, these aims are not achievable without an education for sustainable development approach, says SAM.
Currently, the IAMQS covers qualifications in metal additive manufacturing processing for operators, designers, supervisors, inspectors, coordinators, and engineers, alongside one qualification in polymers for designers. While environmentally-minded elements such as life cycle assessments, waste management and material reuse do appear in these qualifications, there has not yet been a dedicated training program for the sustainability aspects of 3D printing.
The 2020 survey SAM conducted on the analysis of additive manufacturing needs saw more than 100 European training centers delivering 3D printing courses contacted to understand and map the educational practices employed. Through this survey it was possible to assess the mostly addressed skills, namely: technological (AM related), green, digital and entrepreneurial.
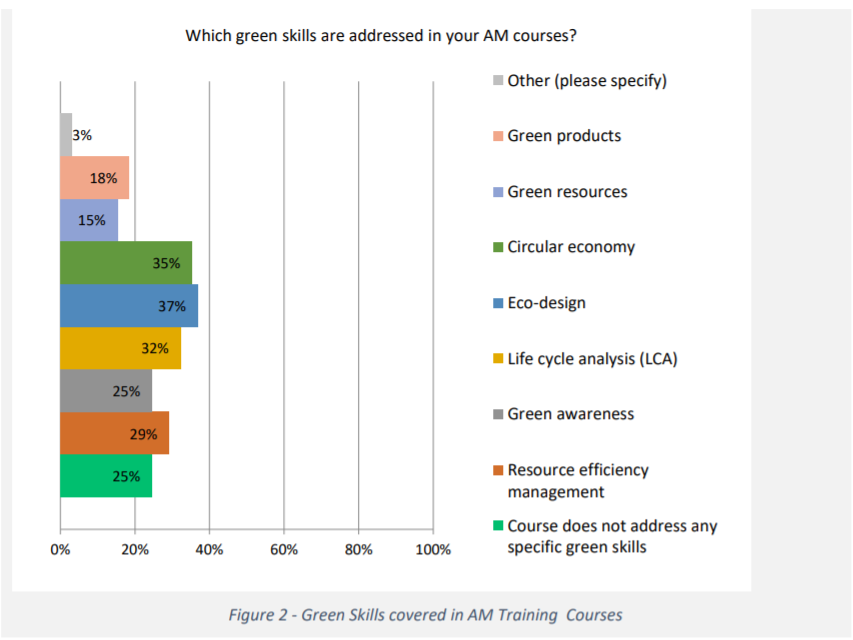
The so-called “green skills” identified by the SAM project are related to resource efficiency, green awareness, life cycle assessments, eco-design, circular economy, green resources, and green products. The survey identified that eco-design (37%), circular economy (35%), and life cycle analysis (32%) were the “green skills” most addressed by current 3D printing training courses.
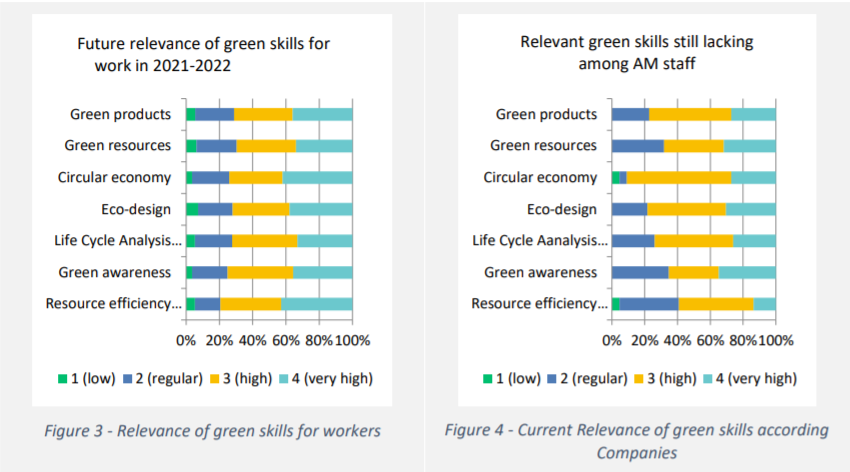
For workers, the top three green skills which should be covered in additive manufacturing training courses are eco-design, circular economy and life cycle analysis, the survey revealed. A similar perspective was shared by managers, with 86% of those who took part in the survey wishing for green skills to be developed within their workforce.
A new training unit for sustainability
After validation by the Industry Council, one of the pillars of the European Observatory, the SAM consortium decided to develop a training unit on sustainability for additive manufacturing, within which green awareness, circular economy and life cycle assessments will be covered. The course is designed to raise the awareness of all 3D printing professionals ranging from operators to designers and engineers.
The course is aligned with the European Qualifications Framework (EQF) level 3, and aims to provide students with a basic knowledge of the economic and social context of sustainability policies, such as the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), and how to incorporate sustainability throughout a product’s life cycle.
Students on the course will also learn how the additive manufacturing industry is currently implementing sustainable practices, as well as their limitations and advantages. Skills-wise, the course will teach participants how to spot ideas and opportunities for more sustainable processes and methods within 3D printing operations, and help them to identify cases for which 3D printing could lead to more sustainable products.
Practically, the course will take a recommended seven hours to complete, corresponding to 14 hours of workload when including self-study. At the end of the course, the participants’ knowledge and skills concerning sustainability in additive manufacturing will be assessed via a short multiple choice written assessment.
Further information on the additive manufacturing sustainability survey can be found in the paper titled: “Impact of additive manufacturing towards the environmental sustainability”, co-authored by S. Masurtschak and A. Almeida.
The SAM project also has another survey underway aimed at Research and Development organizations, called: “Survey on AM Skills & Trends for RTO’s”, which interested parties can take part in here.
Subscribe to the 3D Printing Industry newsletter for the latest news in additive manufacturing. You can also stay connected by following us on Twitter and liking us on Facebook.
Looking for a career in additive manufacturing? Visit 3D Printing Jobs for a selection of roles in the industry.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel for the latest 3D printing video shorts, reviews and webinar replays.
Featured image shows “Green skills” addressed by current additive manufacturing training courses. Image via SAM project.



