Italian 3D printer manufacturer ROBOZE has introduced a new amorphous thermoplastic polyimide filament for its ARGO production 3D printers. Named EXTEM™ AMHH811F, the material has made in collaboration with global chemicals producer SABIC. The new filament is highly heat resistant and flame-retardant, and is, in some cases, intended to replace metals in extreme applications. Keith Cox, SABIC’s senior business manager for Additive Manufacturing, commented:
“To enable customers to print high quality parts for a range of demanding high heat applications, SABIC and ROBOZE have worked closely together to optimize print parameters and secure UL recognition for EXTEM parts printed on ROBOZE ARGO production 3D printer.”

3D printing materials at SABIC
Founded in 1976, SABIC is a global manufacturer in diversified chemicals headquartered in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. The company has operations in over 50 countries in key end markets such as construction, medical devices, packaging, agri-nutrients, electrical and electronics, transportation and clean energy.
It has developed a number of materials for additive manufacturing. Most recently the company launched a breakaway material for FFF 3D printers. In 2018 SABIC also released three new FFF filaments for end-use and prototyping purposes.
ROBOZE has worked with SABIC on a prior occasion, collaborating to develop an FFF polycarbonate filament for ROBOZE’s 3D printer platform in 2018. The material is characterized by high impact resistance and ductility at low temperatures (up to -30° C).
Replacing metals with heat resistant 3D printing filament
Partnering once more, SABIC’s EXTEM AMHH811F filament is now available to use with ROBOZE ARGO 3D printers. The ARGO 500, launched during Formnext 2017, features a print volume of 500 x 500 x 500 mm, and is geared towards production for the aerospace, automotive, and industrial sectors.
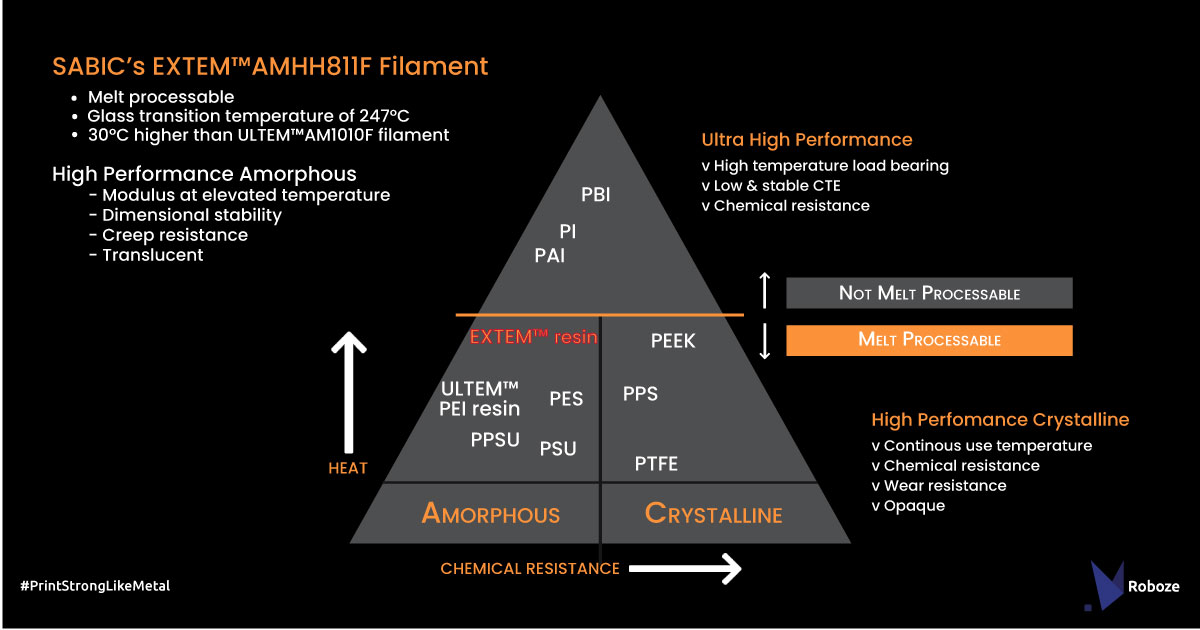
The EXTEM AMHH811F material is a semi-transparent thermoplastic polyimide (TPI). It is characterized by its heat resistance, with a heat deflection of up to 230°C, and the ability to maintain its mechanical strength at high temperatures. It also has a 247°C glass transition (Tg) temperature. Furthermore, the material is flame-retardant, has good chemical resistance and ignition resistance, as well as excellent dimensional stability and easy processability.
In addition, the EXTEM filament has achieved the Blue Card recognition from UL, a global safety consulting and certification firm based in Illinois, with V0-075 certification on 0,75 mm thick samples printed by the ROBOZE ARGO system. UL’s Blue Card program was introduced in early 2019 in order to provide further product transparency and quality assurance for 3D printing materials.
As such, ROBOZE believes the material can address the needs of high performing metal products such as thermal and acoustic shields, enclosures for electronic components and sensors for electric vehicles. Alessio Lorusso, ROBOZE CEO & Founder, concludes: “With ROBOZE ARGO Production 3D Printers and the new EXTEM™ AMHH811F filament, we can increase the opportunities for Metal Replacement. I’m definitely sure that all this will guarantee great advantages in terms of speed and productivity for the users.”
ROBOZE will be premiering the first EXTEM AMHH811F 3D printed parts during Formnext 2019, at booth 121-C61.
Subscribe to the 3D Printing Industry newsletter for the latest news in additive manufacturing. You can also stay connected by following us on Twitter and liking us on Facebook.
Looking for a career in additive manufacturing? Visit 3D Printing Jobs for a selection of roles in the industry.
Featured image shows 3D printed part with EXTEM AMHH811F filament. Photo via ROBOZE.


