Berlin-based 3D printing startup Quantica has announced the integration of MultiSlice, a new artificial intelligence (AI)-based software, into its NovoJet multi material 3D printing technology.
Developed by Charles University spin-off Additive Appearance, the software reportedly offers reliable simulation of 3D models and enables users to accurately manufacture multi-material end-use parts.
MultiSlice will be introduced with Quantica’s new NovoJet OPEN 3D printers launched in November 2023.
“With the trend in 3D printing going to more and more printheads, existing software is starting to limit the hardware’s potential. The problem of which material to put in which voxel is getting increasingly difficult,” commented Tobias Rittig, Additive Appearance’s Chief Technology Officer. “This is why a radically new approach based on cutting-edge research and modern software technologies, such as differentiable computation and machine learning, is required to drive the printers of the future.”
“We both share this realization and are looking to create a synergy of software and hardware that unlocks many new possibilities in the material-jetting domain.”

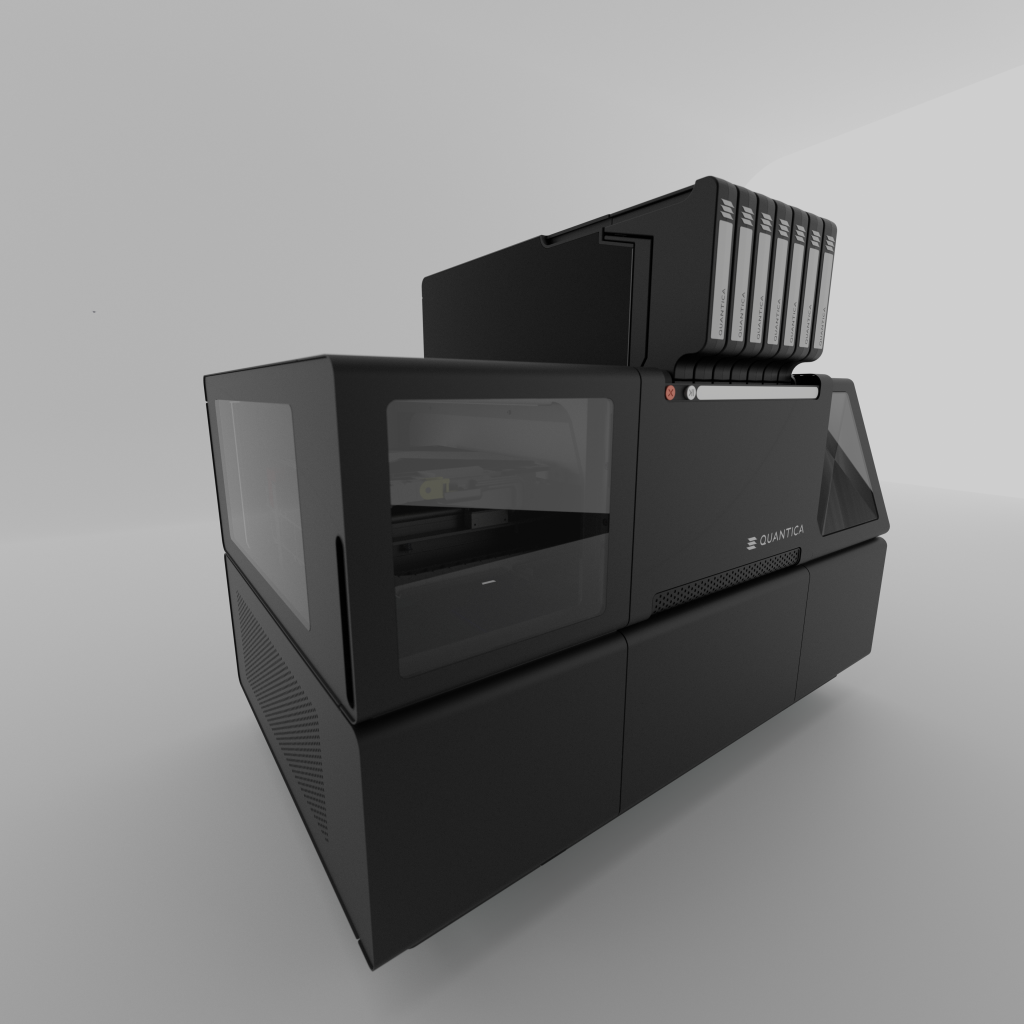
The new NovoJet OPEN
Launched during Formnext 2023, Quantica’s NovoJet OPEN 3D printer incorporates the company’s proprietary NovoJet inkjet printhead.
Manufactured by Inkjet technology developer Xaar through a commercial partnership, these printheads offer wide-ranging functional material compatibility. This includes materials with ultra-high-viscosity, high particle load materials, large particle size and conductive pastes.
These capabilities are said to be “unparalleled” by other inkjet printheads on the market. What’s more, Quantica’s new 3D printer allows users to combine functional materials, on a voxel level, to fabricate multi-material parts in a single 3D print job.
Formnext 2023 also saw the initiation of a Beta Program for the NovoJet OPEN. Partners for this program include the Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Engineering and Automation IPA, and Australian polymer company REHAU Industries.
These partners are working to validate materials for the NovoJet OPEN, develop applications, and fine-tune 3D printer parameters. The beta users are exploring applications in industries ranging from dental to 3D printer electronics.

MultiSlicer to support NovoJet 3D printers
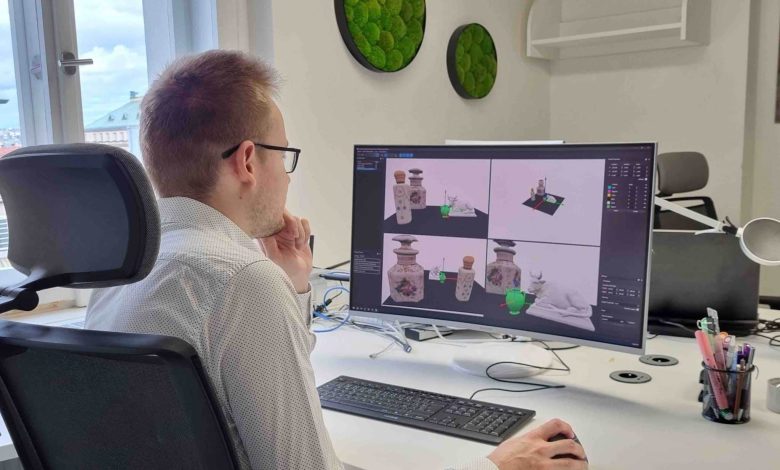
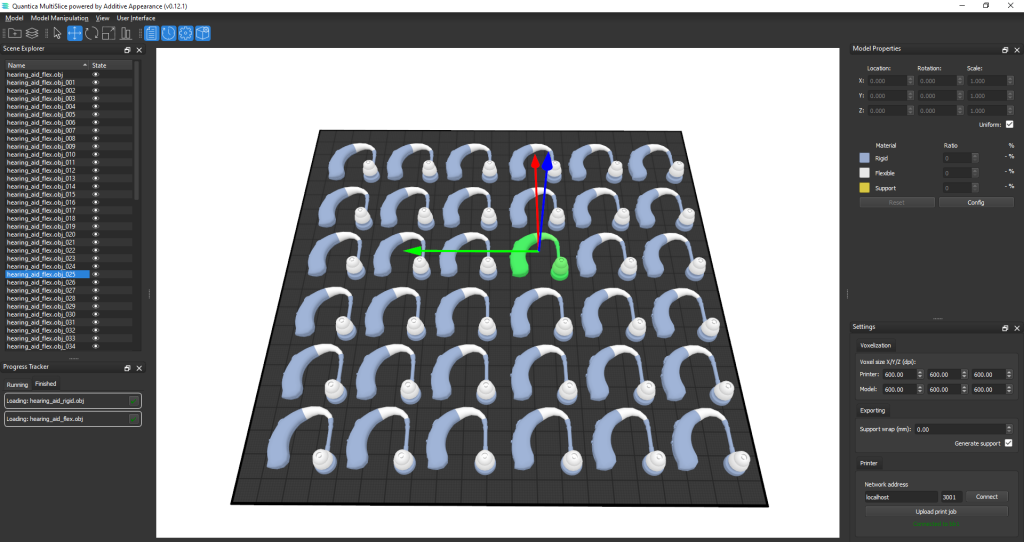
The first NovoJet OPEN 3D printer’s are set to be shipped in Q1 2024, and will be equipped with MultiSlice. This new build management and slicing software will enable users to simulate and replicate both the shape and functionality of their 3D printed parts.
According to Quantica, MultiSlice employs advanced algorithms and AI to make highly accurate 3D model predictions. These capabilities have been developed by expert Computer Graphics researchers at the Faculty of Mathematics and Physics at Charles University.
Looking to the future, Quanitica and Additive Appearance now plan to develop NovoJet OPEN technology to achieve greater control of physical properties on a voxel level. These will include mechanical properties, such as flexibility and conductivity, and visual properties like color.
“Both our companies, embodying the agility of startups, are uniting to redefine the potential of 3D material jetting. In a landscape where functional, multi-material 3D printing lacks adequate software, we are excited to collaborate with a team that is leveraging modern approaches to developing complex software,” stated Grace Chang, Quantica’s Head of Product Management.
“Our collaborative goal is to leverage these advancements, making functional, multi-material 3D printing more accessible, efficient, and adaptable.”
New 3D printing software
Besides Quantica and Additive Appearance, a number of companies have recently launched new software offerings to optimize 3D printing.
3D printing software company Castor recently unveiled a new AI-powered software that can automatically convert 2D drawings into a simulated 3D model. This is said to make the transitioning of 2D drawings to 3D printing efficient, faster, and more accessible.
The software offers a swift Geometric Analysis, and considers material properties, cost-effectiveness, and digital supply chain benefits. As such, Castor’s new software simplified the selection process for suitable parts within seconds. As such, this software reportedly enables a marked reduction in time-to-market for additive manufacturing projects.
Elsewhere, Cloud and API-based 3D engineering platform provider Metafold recently announced an update for its proprietary software. These new features include compression simulation, conformal mapping for lattice structures, and alterations to both the user interface (UI) and API.
The updates are said to improve the accessibility of design for additive manufacturing (DfAM), promoting wider acceptance of 3D printing and lightweighting over conventional manufacturing methods.
Subscribe to the 3D Printing Industry newsletter to keep up to date with the latest 3D printing news. You can also follow us on Twitter, like our Facebook page, and subscribe to the 3D Printing Industry Youtube channel to access more exclusive content.
Are you interested in working in the additive manufacturing industry? Visit 3D Printing Jobs to view a selection of available roles and kickstart your career.
Featured image shows a user operating the MultiSlice software. Photo via Quantica.


