A newly published patent from Made in Space describes several systems that could be used for 3D printing in space. These include, “a system and method for assembling a spacecraft such as a satellite in space.”
Michael Snyder, Chief Engineer and co-founder at Made in Space, is named as inventor on the patent.
The challenge of 3D printing in space
In the 64 page document Made in Space explains one challenge to 3D printing as, “the severely limiting problem where no object can be produced larger than the machine that is creating it.”

During last years International Astronautical Congress (IAC) in Mexico, the topic of off-world fabrication was the subject of several seminars. Approaches raised during the IAC event included the use of metal wire deposition 3D printing methods in space, of particular interest was that the inert atmosphere found in space would permit a substantially expanded build area.
The Made in Space patent includes the description of a 3D printing system where, “the build area is an unlimited build area in at least one axis where the object is produced.” As 3D Printing Industry reported, progress on the commercialization on earth of systems such as the Infinite Build from Stratasys are also looking at ways to increase build volume.
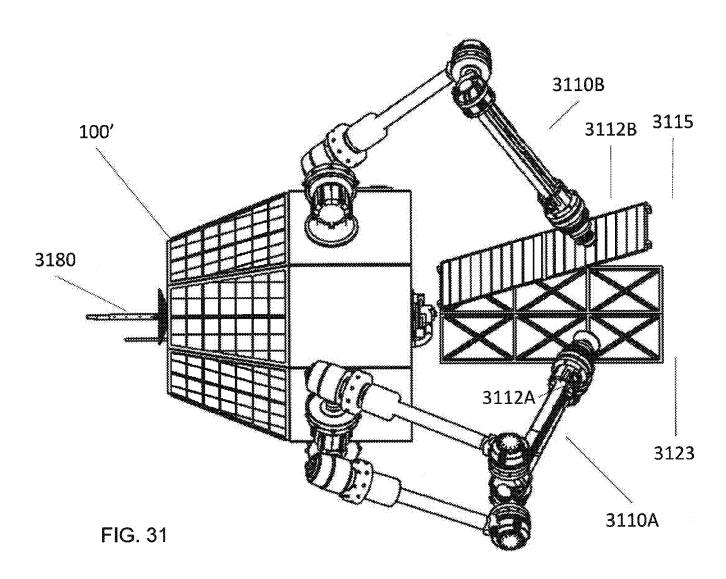
Extended structure additive manufacturing
The patent describes a technique called extended structure additive manufacturing (ESAMM). This 3D printing technique may have applications in space but also in microgravity and nautical environments. A description of the 3D printing method reads,
A system comprises a build device having a build area and a material bonding component to receive portions of a material that are used to produce the object, at least one gripper within the build area to contact the object to provide support and to provide for at least one of a heat sink for the object. The system also comprises a cold sink for the object, and electrical dissipation path from the object. The system further comprises a movement mechanism to move the build device relative to the object to position the build device at a position to further produce the object.
The method proposed by Made in Space is intended to overcome current challenges such as the limited launch volume and mass of spacecraft. Furthermore, “when a spacecraft is deployed from earth it undergoes significant forces which can cause systems to become non-operational once in space.”

Earlier this year 3D Printing Industry asked Justin Kugler, business development engineer at Jacksonville Florida’s Made in Space about plans for the future of additive manufacturing in space.
The full Made in Space patent is available online. For all the latest news about 3D printing, subscribe to our newsletter and follow our active social media channels.
Featured image shows views of an extended structure additive manufacturing device for manufacturing a spacecraft in space. Image via Made in Space.



