The metal powders for additive manufacturing market continues to see increased competition with the acquisition of Metasphere Technology by Höganäs.
Based in Luleå, Sweden, Metasphere was founded in 2009 and uses a combination of plasma and centrifugal forces to atomize metal and produce spherical metal powder.
The powder has a range of uses including surface coating and additive manufacturing.
Gearing up for production
The terms of the deal, and the specific details of the technology have not been disclosed. However Fredrik Emilson, Höganäs CEO, said, “Metasphere’s technology is unique and innovative.
The plasma atomization technology developed by Metasphere can be used to atomize metals, carbides and ceramics. Operating at “very high temperatures” the groundbreaking reactor has so-far primarily been used to make powders for surface coatings. However as scale up for industrial production begins the focus will be “mainly within additive manufacturing, where there is a large demand for innovative materials,” explained Emilson.
Höganäs says that production capacity has not yet been finalized, and work will begin on the production reactor in Q1 2018.
Increasing adoption of additive manufacturing
Headquartered in Sweden, Höganäs are the world’s largest producer of powdered metal products. In the metal powder for additive manufacturing market a fellow Swedish company, Arcam via subsidiary AP&C, is one of the current leaders in production of such materials.
The materials market has seen much activity in 2017, with companies including Alcoa, LPW, GKN and PyroGenesis all advancing during the year. PyroGenesis is a particularly interesting company, given their expertise in this field as the developers of the IP in use by AP&C.
Also notable are advances in software aimed at reducing the amount of metal powder used during 3D printing. For example the recent launch of e-Stage for metal by Materialise.

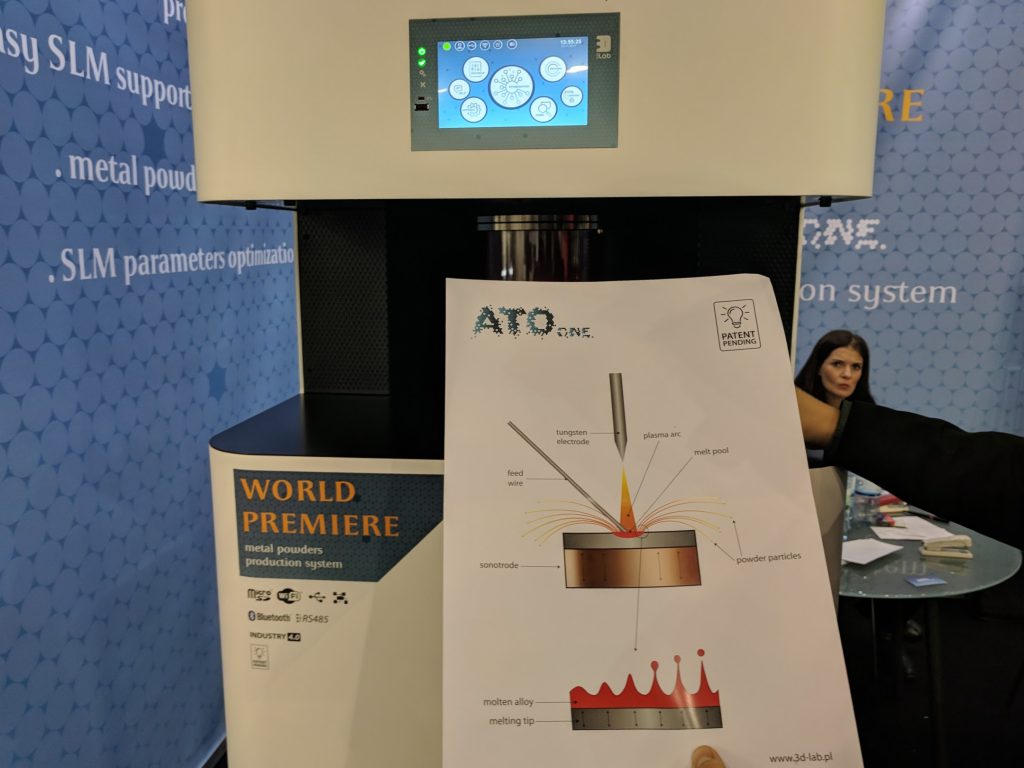
One novel enterprise also making metal powders is Poland’s 3D Lab. Their ATO One machine is aimed at users who require smaller batches of metal powder materials – for example research labs – and is billed as “office friendly.”
Increased competition in the materials market is a welcome development, with the end result hopefully a wider palette of materials to work with and also lower price points.
Both are factors that will encourage the wider application and adoption of additive manufacturing.
Nominations for the second annual 3D Printing Industry Awards are now open. Let us know which materials companies are leading the additive manufacturing industry now.
For all the latest 3D printing industry news, subscribe to our free 3D Printing Industry newsletter, follow us on Twitter, and like us on Facebook.
Featured image shows Urban Rönnbäck, founder of Metasphere Technology in Luleå, and Fredrik Emilson, Höganäs CEO.


