The European Space Agency (ESA) has awarded a contract to Europe’s largest industrial automation specialist, Siemens, in order to develop an aerospace design and production software for metal 3D printing.
Siemens will be part of a two-year long project called Design4AM, alongside Sonaca, a Belgian aerospace company.
Pedro Romero Fernandez, Sonaca General Manager Space BU, said, “With our deep aerospace knowledge and Siemens’ software technologies such as generative design, automated topology optimization and additive manufacturing process simulation,”
“engineers will be able to explore hundreds of design options in a fraction of the normal time, then virtually test them against a variety of physical conditions to arrive at the best design solution for their performance requirements that 3D print correctly the first time.”
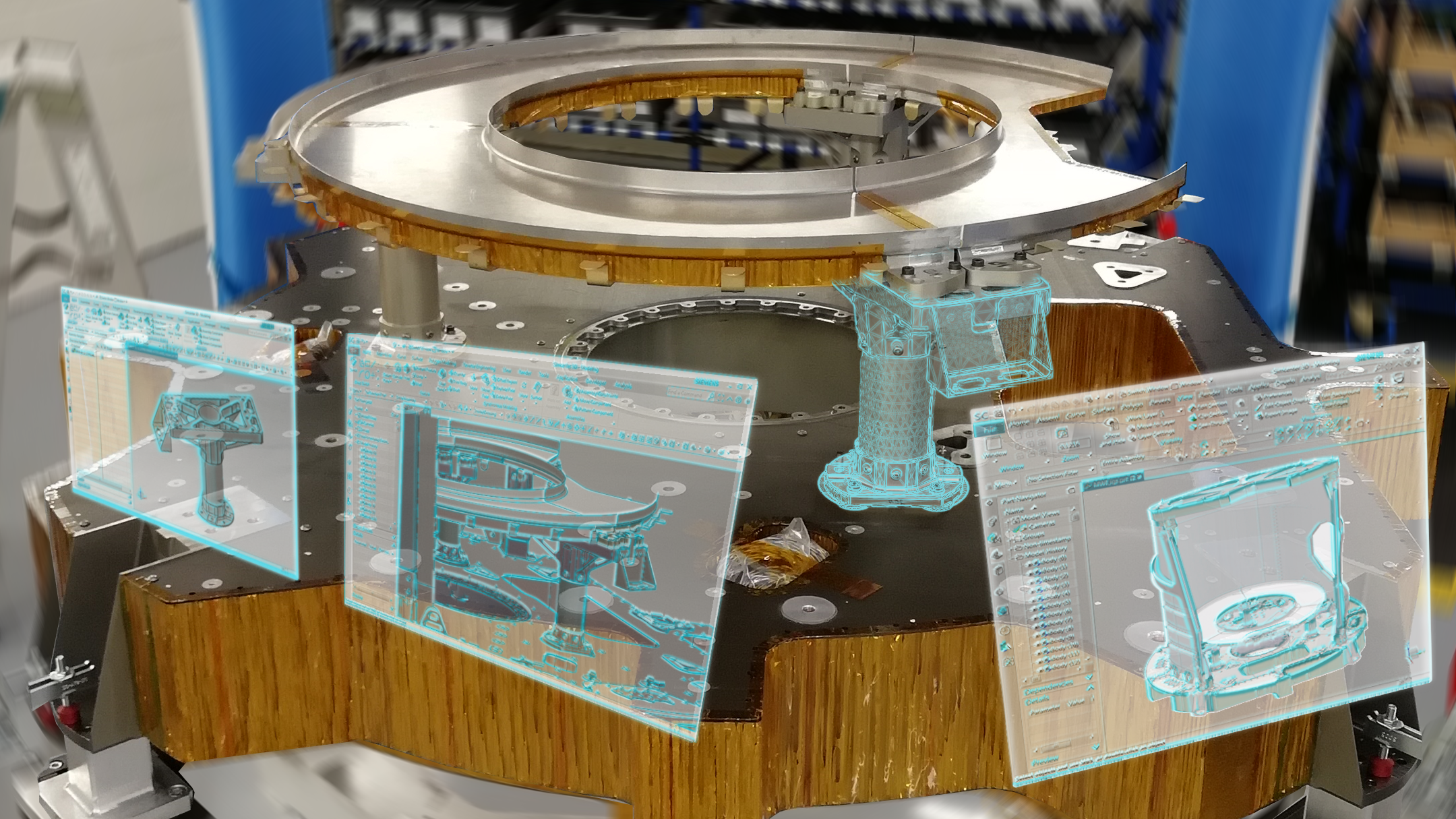
Siemens additive
Siemens is the largest industrial manufacturing company in Europe. In the additive manufacturing sector, the German company has made significant investments. Recently, it partnered with the German automotive engineering service the EDAG Group. The collaboration, with the help of 3D printing, aims to reduce lead times for prototyping and manufacturing small components in the automotive industry. This partnership also includes Constellium, a manufacturer of aluminum products, and Concept Laser, a GE Additive-owned metal 3D printer manufacturer.
Furthermore, Siemens also owns Materials Solutions, a UK-based metal 3D printing specialist, who recently opened a ‘Digital Factory’ aimed at automating AM production. The smart factory houses nineteen 3D printers to serve the automotive and aerospace industry.
As a metal 3D printing specialist, Siemens has also collaborated with Solukon Maschinenbau to manufacture the SFM-AT800S, a system used for de-powdering parts 3D printed with a powder bed fusion machine. Currently, Siemens is modifying its Sinumerik ONE CNC controller for use in BeAM‘s Modulo 250 DED machine.
In addition to hardware, Siemens has dedicated 3D software which includes Solid Edge and Siemens NX for CAD and CAM and Simcenter for computer-aided engineering (CAE) simulation.

Making space possible
With ambitions to conduct interplanetary missions, ESA is rapidly adopting 3D printed technology for its space program. One of the benefits of using metal 3D printed parts is that they are lighter than components made using subtractive and other traditional methods. And lighter parts affect the size and costs of payloads which are important determiners in space flights.
The Design4AM project is funded by ESA and the Belgian Federal Science Policy Office (Belspo). It will be concluded with the completion of a comprehensive software for producing metal 3D printed components which are lightweight and have applications in the space industry. The software will be based on Siemens NX and adopt Siemens’ Digital Innovation Platform framework. It will be equipped with relevant design and production tools such as generative design, predictive analytics, process simulation, and build preparation.
On how the Design4AM project will benefit ESA, Didier Granville, RTD projects Manager for Siemens in Liege, explained, “Additive manufacturing can help ESA reshape everything for optimal performance at reduced cost, in comparison to traditional manufacturing methods that require multiple steps, tools, and treatments to achieve the desired outcome,”
“Working with Sonaca, we will be able to help ESA take advantage of additive manufacturing to deliver high-performance structures capable of withstanding the extreme forces that occur during space satellite launches.”
Subscribe to our 3D printing newsletter to learn more about metal additive manufacturing and join us on Facebook and Twitter.
Looking for a job in manufacturing? Visit our 3D Printing Jobs page.
Featured image shows an engine designed in Siemens NX. Image via Siemens.

