Automotive manufacturer Audi have announced a new partnership agreement with fellow German company, 3D printer manufacturers EOS. The use of additive manufacturing will be used for, “equipment and prototype building at Audi, as well as motor sports, where the technology is already in use today.”
EOS are one of the largest 3D printing companies, known for their industrial-sized Direct Metal Laser Sintering machines.
The agreement between the two industry-leading companies follows a call from the German Government to advance new digital technologies in industry. Earlier this year the German Federal Minister of Transport and Digital Infrastructure, Alexander Dobrindt, encouraged a new government department to be created, known as the Federal Ministry of Digital. 3D Printing Industry also reported the news that Siemens have partnered with Trumpf in recent weeks to advance the industrialization of additive manufacturing.
Audi incorporating Additive
The German automotive manufacturers are developing their 3D printing center in the southern city of Ingolstadt. The flagship plant is home to Audi’s largest production facility and Europe’s second-largest car factory. It produced over 500,000 cars in 2015 and so EOS can expect their machines to be busy at the plant. Audi are looking at the EOS collaboration in order to further their tool manufacturing process.
Güngör Kara, Director of Global Application and Consulting at EOS, explained how the agreement will move Audi forward,
The aim is to not only supply Audi with the right additive systems and processes but to also support them during applications development, when building up internal AM knowledge and training their engineers to become in-house AM experts.
According to Audi, a large factor for their expansion in to 3D printing is the increased manufacturing possibilities that it creates. Audi are excited since “the technology will make possible the production of geometries that would have to be joined in conventional manufacturing.” This is a commonly cited advantage of 3D printing.
3D Printing Industry recently reported another new research project focused on the production of car components using additive manufacturing. The University of Nottingham are undertaking a new project to create fuel-efficient functional lattices for automotive components. This research will demonstrate the possibilities of creating strong 3D printed components that are also lightweight and energy efficient.
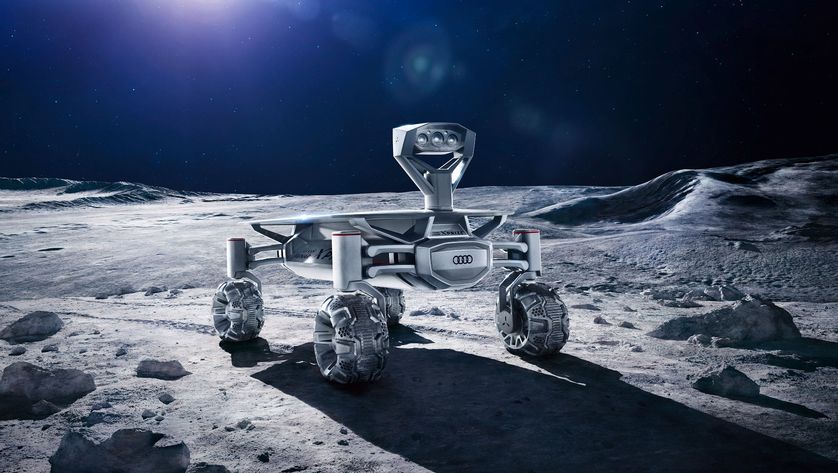

Audi have been also featured on 3D Printing Industry recently for their extra-terrestrial 3D printed plans. Collaborating on a design process for creating a Lunar Rover, called ALINA, with the Part Time Scientists. One element of this project will put a 3D printing microwave on the moon. While EOS won’t be working on ALINA, perhaps it opened the eyes of the German automotive company to the possibilities.
Another motive for Audi’s new approach is sustainability. In contrast to traditional manufacturing techniques, additive is a considerably more ecological process as it creates less material waste. The aim to create more sustainable cars is common in top automotive companies but now many companies are looking towards carbon friendly manufacturing methods. 3D printed car creators, Divergent, believe additive manufacturing reduces emissions significantly in comparison to conventional techniques.
Audi’s Head of Toolmaking, Jörg Spindler, explains the immediate plans for this partnership with EOS,
With this technology we are able to integrate internal structures and functions in tools that we have not been able to create so far with conventional manufacturing methods. Especially with components in small batches, we can now produce components using lightweight construction, quickly and economically based on this technology.
Featured image shows the Audi RSQ concept car. Photo via MotorAuthority.



