In this edition of Sliced, the 3D Printing Industry news digest, we cover the latest business developments, partnerships, and acquisitions across our industry.
Today’s edition features software updates, additive manufacturing partnerships, new 3D printers and materials, an online 3D printing education platform, a number of certifications, 3D printing prototyping technology, and a way to automate orthosis devices with 3D scanning.
Read on for the most recent updates from DDM, Stratasys, Alloyed, PRES-X, Sandvik, CREATE, Linde, and more.
Software updates in additive manufacturing
New York-based engineering software developer nTopology recently implemented support for the 3MF file format on its nTop platform, allowing users to export parts as beam elements with a significantly reduced file size. Engineers, when designing complex geometries, often face file size and image resolution problems. The open-source format allows users to export files into programs like Materialise Magics at ⅓ of the usual STL file size for the same geometries.
“As one of the founding members of the 3MF Consortium, we are excited about this connection with nTopology,” said Stefaan Motte, Vice President of Software at Materialise. “Beam lattices represent a first step, but there is still a lot of potential to extend the 3MF standard in order to create a more streamlined process.”
CADENAS, a German software developer, and Danish printing equipment supplier AddiFab have announced plans to combine their technologies to accelerate the production of prototype tools. AddiFab’s Freeform Injection Molding process will be coupled with CADENAS’ GEOsearch, a geometric similarity search engine, allowing engineers to start from a 3D sketch and rapidly identify components that are geometrically similar in the GEOsearch libraries. The idea is that this will streamline the prototyping process and lead to reduced delivery times.
“3D printing leads to great savings through shorter delivery times and very low entry costs. With PARTsolutions, we may provide users of Freeform Injection Molding with an ideal solution for prototype production and small series production for injection molding,” said Lasse G. Staal, CEO at AddiFab.

3D printing partnerships for Signicast, DDM, and Team Penske
Starting with the latest collaborations, US-based digital manufacturing company DDM signed a strategic partnership with investment casting specialist Signicast. The latter specializes in rapid in-house tooling, direct metal laser sintering, and stereolithography (SLA) patterns for design validation. DDM’s LAMP (Large Area Maskless Photopolymerization) ceramic 3D printing technology is set to serve as a significant contribution to Signicast, allowing the company to quickly develop components that are more ergonomic, lowering material costs.
“DDM is extremely proud to join hands with Signicast to modernize investment casting while offering speed, complexity, and value to customers,” said Dr. Suman Das, Founder, and CEO of DDM. “This partnership greatly accelerates the introduction of DDM’s ceramic 3D printing based Digital Foundry offering to the market.”
Team Penske, often referred to as the New York Yankees of motorsport, and 3D printer manufacturer Stratasys recently extended their longstanding technical partnership. Both US-based companies have been collaborating since 2017, and the extension of their partnership will enable Penske’s NASCAR, INDYCAR, and IMSA teams to continue utilizing Stratasys’ FDM and PolyJet technology.
The difference made by the implementation of Stratasys’ technology was made clear by Matt Gimbel, Team Penske’s production manager: “The Stratasys partnership has allowed us to not only increase our output but also to produce parts in new materials that are immediately installed on race cars. As a result, we have more design freedom and manufacturing speed to iterate faster to reach the optimum design.”

Metal alloy specialist Alloyed and TANIOBIS, a global producer of tantalum and niobium, also entered into a collaborative alliance that will result in a full end-to-end material development project. Alloyed is born out of a merger of OxMet Technologies and Betatype, whilst TANIOBIS is part of the JX Metals Group. Together their aim is to research and develop novel titanium and refractory alloys to expand the material options for additive manufacturing.
“There is great synergy between TANIOBIS and Alloyed that I believe will serve our clients in limitless ways when it comes to proving end-to-end solutions for new and greatly improved applications with metal AM technologies,” said Katarzyna Kosowski, Head of Corporate Bussiness and Communication at TANIOBIS.
Updates on 3D printer investments
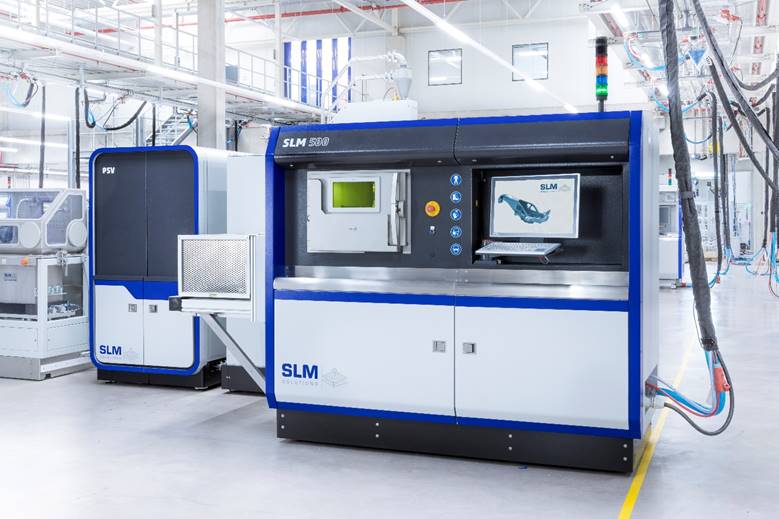
Howco, a global distributor of raw materials for the oil and gas industry, placed its first order for the SLM500 3D printer from German manufacturer SLM Solutions. The printer, intended for Howco’s AM facility in Texas, is a selective laser melting machine renowned for its integrated SLM Build Processor and software architecture. The printer has a 500 x 280 x 356 mm build chamber and four overlapping lasers delivering 1600W of power. Compared to twin laser configurations, building rates are increased by up to 90% with quad laser optics.
“We went through an extensive selection process over a number of months to make sure we had the optimum technology for our new venture. We are expecting delivery in Q3 2020 and we are working hard to have our ancillary support equipment in place to allow us to start printing components,” said Conrad Kao, Director of additive manufacturing at Howco.

High-pressure technology company Quintus Technologies also recently delivered the QIH 60 M URC to Italian start-up PRES-X. PRES-X serves customers across the aerospace and automotive industries with an aim to reduce operational in additive manufacturing production lines. The printer is a fan-driven hot isostatic press (HIP), featuring a hot zone of 16.14 x 39.37 inches (410 x 1,000 mm) and functions at a maximum temperature of 1,400℃. The maximum pressure is 207 MPa and it has 600kg of workload weight capacity.
“The QIH 60’s innovative capabilities have already prompted customers to review their parts production methods, even in application areas that have long used more traditional techniques,” said Andrea Scanavini, CEO and Founder of PRES-X. “This is allowing us to see new project starts and growth in orders and revenue despite a very challenging global market situation.”
3DPRINTUK, a 3D printing service provider, is continuing to expand its range of 3D printing machinery, this time with an investment in two EOS Formiga P396 machines. This purchase is the fourth step in a £1 million expansion plan created by the company. The previous steps included the purchases of the SLS Flexible material, and the P100 and P110 SLS machines. With the latest investment, the company now expects to have a 38% reduction in energy consumption and considerably reduced downtimes between builds.
“We are excited to introduce two P396 machines into our new expanded premise in London,” said Nick Allen, CEO at 3DPRINTUK. “We can now offer the full 300 mm x 300 mm x 600 mm capacity on the P396s following considerable testing in the real world. This is all part of an on-going £1 million strategic expansion plan at 3DPRINTUK, and we will be making more announcements in the near future.”
Online facilities: CREATE relaunches online platform for 3D printing
CREATE education, abbreviated from community, reliability, education, access, teachability, and economics, is a company dedicated to global 3D printing education. It is now relaunching its online platform and STEAM education qualified technology. The platform, CREATE Connect, is open to anyone interested in learning about the world of additive manufacturing, from children to experts. The ‘Learn 3D Printing’ section gives users the opportunity to browse resources and guidance, whereas the marketplace section provides the opportunity to purchase products.
“Whether you are new to 3D printing or an established user, there will always be times when you need a little help. CREATE Connect enables our community members to discuss projects, share ideas, advice, insights and best practices,” said a member of the CREATE Education team.
New post-processing offerings by 3DPRINTUK
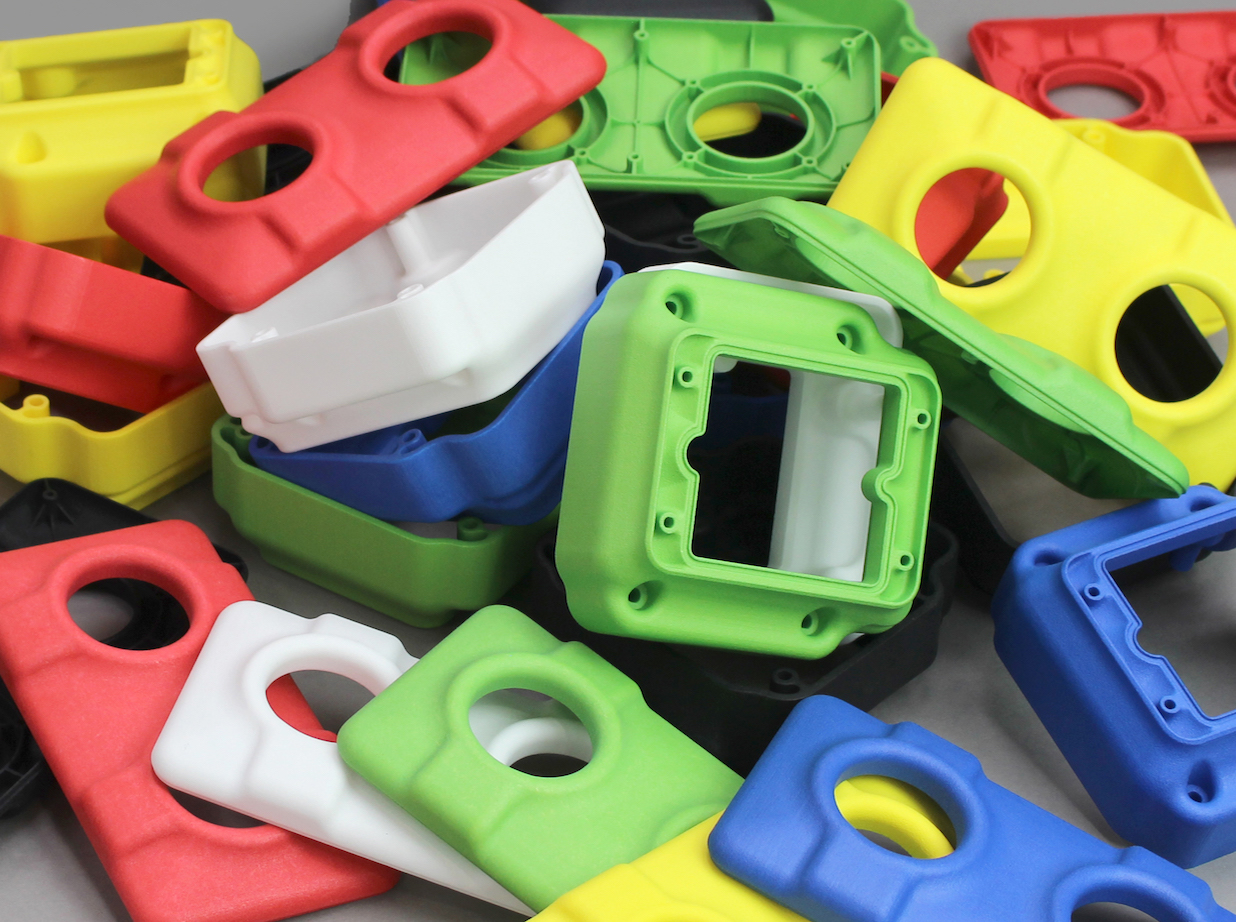
3DPRINTUK has also introduced new color options for its services by investing in Dyemansion’s DM60 dying machine. As of recently, the company has also acquired the PrimePartST flexible PEBA which enables flexible and rubber-like materials such as Nylon 12, and a shot peening service intended for low, medium, and high volume part production. The £50K investment in the DM60 machine, coupled with the company’s experience in testing, means they can now offer parts in red, green, blue, and yellow.
Nick Allen, CEO at 3DPRINTUK said that in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, “we reacted by further refining our 3D printing services in order to offer an expanded and versatile palette of options for our customers. We have now invested over £100K in dying systems, ensuring that we respond to customer demand and continue to provide the most comprehensive PBF production capabilities.”

Gas mixture developments from Linde
Global engineering company Linde recently announced the release of ADDvance Sinter250, a new gas mixture tailored for Desktop Metal’s Bound Metal Deposition process. The gas mixture consists of argon and hydrogen and can be used with parts made of stainless steel. US-based Desktop Metal has stated that it will use the mixture for its new Studio System, a printer intended for offices, and smaller working environments. The temperature regulation it provides prevents the parts from discoloring and losing strength, whilst maintaining high surface quality.
“Linde has developed a standard gas offering optimized for Studio System, and is able to offer this streamlined solution to our European Desktop Metal customers,” said Arjun Aggarwal, Desktop Metal’s VP of Business Development & Product. “This enables us to expand our horizons and bring added value to our business.”
Medical News: 3D scanning to automate orthosis
A german orthopedic clinic recently turned to 3D scanner manufacturer Phoenix GmbH & Co to help automate the process of creating foot orthoses – external medical devices capable of regulating biomechanical alignment and correcting deformation. The traditional orthopedic method has multiple underlying drawbacks, such as being time-consuming and requiring constant revision.
By introducing 3D scanning into the mix, the doctors are able to scan an existing positive form of the foot with Phoenix’s Calibry 3D scanner, and then thermoform the orthosis shell in a vacuum – a process that is expected to reduce doctors’ workloads by around 40%.
Emil Worgotter, Application Engineer in 3D Scanning and Additive Manufacturing, said that “Before Calibry, we had to use more expensive, less user-friendly scanners to do the same tasks. This is a limiting factor in B2B scanning applications; where the user is no scanning expert.”

Certifications and patents in the 3D printing industry
Sandvik, a Swedish metal powder company, recently received the ISO 13485:2016 medical device certification for its Osprey titanium powder at its powder processing facility, certifying that the company is operating in a regulated environment. The facility, inaugurated in 2019, also contains a complete in-house supply chain for the production of medical devices, allowing for easier traceability and control.
“Now we are one of the few metal powder and additive manufacturing companies holding both the AS9100D quality certification for aerospace and the ISO 13485:2016 certification”, said Keith Murray, VP, and Head of Global Sales at Sandvik Additive Manufacturing. “This will facilitate many customer collaborations going forward.”
PostProcess Technologies, a global provider of post-processing systems for 3D printed parts, recently received a U.S. patent for its Submersed Vortex Cavitation (SVC) technology. The patent, issued on August 11, covers the software and hardware required to make the mechanical support removal system operational.
“The issuance of this patent is confirmation of the ground-breaking work we’ve undertaken over the many years here at PostProcess,” said Daniel J. Hutchinson, inventor of the SVC technology and Founder and CTO at PostProcess Technologies. “We’re dedicated to innovating cutting-edge solutions that will transform our customers’ workflows.”
Nominations for the 2020 3D Printing Industry Awards are still open, let us know who is leading the industry now.
The fourth edition of the 3D Printing Industry Awards Trophy Design Competition is now underway. Enter your design for the chance to win a CraftBot Flow 3D printer.
To stay up to date with the latest 3D printing news, don’t forget to subscribe to the 3D Printing Industry newsletter or follow us on Twitter or liking our page on Facebook.
Are you looking for a job in the additive manufacturing industry? Visit 3D Printing Jobs for a selection of roles in the industry.
Featured image shows 3DPRINTUK’s new coloured parts made with DM60 dye machine. Photo via 3DPRINTUK.


