In this edition of Sliced, the 3D Printing Industry news digest, we cover the latest business developments, partnerships, and acquisitions in the additive manufacturing sector.
Today’s edition features new materials, partnerships, and business deals.
Read on for the news and updates from Erpro3D, Arkema, Photocentric, L3 Harris, Chromatic 3D, and more.
Business deals and acquisitions from Erpro3D, Plastigen, Massivit 3D, Stratasys, and more
Diving into business deals and acquisitions, Erpro 3D Factory has achieved a significant milestone by creating an integrated supply chain in Europe to produce custom parts using Arkema‘s bio-based elastomers, Pebax, and Rnew. These innovative elastomers, partially derived from renewable castor beans, are renowned for their use in high-performance sports shoes, consumer electronics, and medical devices. Now, Erpro 3D Factory can manufacture large-scale 3D printed parts from these materials using selective laser sintering (SLS) technology, presenting new possibilities for customers. The collaboration with Arkema marks a groundbreaking improvement over traditional TPU materials, offering enhanced performance and the use of renewable resources. Soon, customers can conveniently order parts made from the new Pebax and Rnew powder through the user-friendly Easy3D platform.
Followed by Plastigen, Chile’s leading industrial polymer supplier and parts manufacturer, has joined the Roboze 3D Parts Network, an AM production network developed by Roboze, an industrial 3D printing systems provider. Through this collaboration, Plastigen will offer qualified 3D printed parts on-demand, using Roboze‘s advanced additive manufacturing systems and materials to support Chilean manufacturers and OEMs. As Chile embraces Industry 4.0 concepts, such as additive manufacturing, this partnership presents an opportunity for local manufacturers to optimize supply chains, reduce lead times, and enhance operational efficiency. By embracing localized 3D printing, Chile can advance towards sustainable and innovative manufacturing practices, reducing waste and energy consumption.

3D printer manufacturer Massivit 3D has introduced a groundbreaking solution for composite production through additive-manufactured mandrels. Additively manufactured mandrels offer advantages over traditional methods, enabling complex designs with reduced lead times and lower costs. Massivit’s proprietary printing process, utilizing water-breakable material, produces strong and durable mandrels that crumble in water, facilitating easy removal from the final product. The Massivit 10000 AM system, employing Cast In Motion (CIM) technology and Gel Dispensing Printing (GDP) method, allows direct casting of the mold into a 3D printed sacrificial shell. This disruptive technology revolutionizes composite part manufacturing, offering higher quality, reliability, and efficiency in various industries.
3D printer OEM Stratasys has unveiled GrabCAD Print Pro, a new software designed to optimize the print preparation process for its polymer 3D printers. Integrated with quality assurance functionality from Riven, a Stratasys acquisition, the Pro version is tailored for manufacturers aiming to efficiently produce end-use parts at production-scale volumes. The software offers advanced capabilities, including automatic warp correction, standardized manufacturing templates, improved cost estimation, label generation, and 3D array features. GrabCAD Print Pro also introduces third-party partner plug-ins, with AlphaSTAR and Castor among the initial partners. Stratasys aims to support customers in scaling up their additive manufacturing capabilities for end-use parts production.
French-Swedish industrial robotics startup ADAXIS has become an Associate Member of the 3MF consortium. The 3MF format ensures data integrity and eliminates fragmentation by encompassing all necessary model, material, and property information within a single archive. ADAXIS will work with other members to optimize the 3MF format specifically for Robotic Additive Manufacturing, aiming to drive advancements in additive manufacturing technology and enhance robotic systems’ capabilities in the industry. This affiliation underscores ADAXIS’ commitment to excellence, innovation, and collaboration, contributing to a more efficient and sustainable future for manufacturing.
Furthermore, Italian motorcycle exhaust manufacturer Termignoni has revolutionized its production process with Stratasys’ industrial FDM additive manufacturing solution. By adopting the Stratasys F770 3D printer in-house, Termignoni drastically reduced time to market for its motorcycle exhausts from weeks to days and cut production costs by 50%. The large build chamber of the F770 allows the entire component to be 3D printed as a single piece, eliminating inaccuracies and inefficiencies associated with gluing parts together. Using ASA thermoplastic and soluble support materials, Termignoni achieved remarkable stability, surface appearance, and post-processing efficiency, enhancing its aftermarket parts development and maximizing sales opportunities.
Ernesto Marinelli, General Manager and Product and Technical Director at Termignoni, says prototyping typically represents a third of the development time. “Being able to 3D print quickly, test, make revisions, and so on creates a definite time advantage,” he says. “Now, the process is simpler, faster, and therefore more cost effective.”
Asahi Kasei is investing in Castor Technologies, an Israeli 3D printing software startup, aiming to capitalize on the fast-growing 3D printing market. With annual growth projected to reach 24%, the need for optimized technical services and faster customer response times is critical. Castor’s software uses proprietary algorithms to automatically select suitable parts for 3D printing from CAD drawings and propose shape modifications, streamlining the manufacturing process. Asahi Kasei’s investment will allow for synergies between its CAE technical service for plastic products and Castor’s software, enhancing support for customer product design and development with more advanced simulations.
“Through this investment, we will further investigate the synergies between CASTOR’s software and Asahi Kasei’s CAE expertise,” said Yukihiro Bann, Senior General Manager for Business Strategy and Marketing, Mobility & Industrial SBU at Asahi Kasei Corp. “We aim to provide our customers with more advanced and automated real-time simulations, as well as to expand the range of technical services that both companies can offer.
Metal 3D printer manufacturer SLM Solutions and Chromalloy are partnering to accelerate additive manufacturing production in the aviation and energy sectors. Chromalloy, a global aviation and energy technology company, has chosen SLM Solutions as its metal additive manufacturing partner and acquired the SLM 280 machine. Leveraging SLM Solutions’ open-architecture technology, Chromalloy will develop high-quality metal parts, with a focus on its proprietary LifeX products and services that optimize engine overhauls. As the leading independent supplier of aftermarket solutions for jet engines and gas turbines, Chromalloy’s expertise combined with SLM Solutions’ cutting-edge technology promises to set a new benchmark in the additive manufacturing industry.
German machine tool manufacturer TRUMPF and Trickstuff, a bicycle company are set to showcase groundbreaking titanium brake levers for bicycles, manufactured using 3D printing technology, at the Eurobike bicycle trade show. The use of 3D printing allows for cost-effective processing of titanium, which has a superior environmental footprint compared to traditional carbon materials commonly used in brake levers. Unlike carbon, titanium is recyclable and more durable, enabling the creation of stiffer and more robust brake levers. Additionally, 3D printing enables customization of the brake levers, including design and lever forces, tailored to the cyclist’s preferences and needs. This innovation promises to revolutionize the bicycle industry and enhance sustainability in bike component manufacturing.
Daedalus Investments, the parent company of Tech Cast Limited, has made an acquisition, purchasing Oklahoma-based ClassIQ Manufacturing. The services provided by ClassIQ cover AM in multiple markets, including the Investment Casting Industry. ClassIQ boasts a notable 35+ years of experience in the field of Additive Manufacturing, establishing a strong reputation within the AM industry and solidifying its position as a leading provider for various AM services, notably SLA Quickcast Investment Casting Patterns.
“Tech Cast has been one of our best customers over the years. We have always admired their innovation and adaptation of AM to provide low-volume, quick- turn investment castings to their customers. This acquisition makes sense, and we are very excited about future opportunities for both Areion3D and Tech Cast Limited,” said Joan Speed, CFO and Owner of ClassIQmfg.
3D printing equipment manufacturer Volkmann USA, has introduced the Modular Powder Supply (MPS), a solution designed to address the challenges of managing metal powder storage in additive manufacturing. The MPS features an inline holding container that connects to printing, sieving, and depowdering processes, allowing efficient collection and preservation of unused metal powder from the build box. This enables faster initiation of the next part without manual extraction delays. The recovered metal powders can be screened and reintroduced to the printing process or stored for future use. The system is available as a standalone unit or can be integrated with Volkmann’s PowTReX metal powder sieving and depowdering stations. It supports various metallic powders and can operate in both normal air environments and under inert conditions.
Private equity firm CORE Industrial Partners has acquired Coining Manufacturing and Precision Machine Products through its portfolio company GEM Manufacturing. The Company, founded in 1990, specializes in progressive die stamping, screw machining, CNC machining, and wire EDM manufacturing technologies to produce intricate precision components. They offer a wide range of services, including piercing, drawing, coining, trimming, tapping, deburring, and bending. Serving the aerospace & defense, medical, electronics, and semiconductor industries, they manufacture various products like microelectronic and sonic packages, sensors, implantable devices, connectors, terminals, solder cups, thermocouple pins, and seal headers. Based in Clifton, New Jersey, the Company operates in an ISO9001-certified facility with more than 60 machines, working with metals such as aluminum, copper, stainless steel, titanium, Kovar, Inconel, Alumel, and Chromel.
Plastic processing machine manufacturer ARBURG, has successfully 3D printed Mechnano’s new Polycarbonate Thermoplastic pellets with static dissipative properties “PC ESD” on their Freeformer line of pellet extrusion Additive Manufacturing printers. Mechnano‘s proprietary technology, D’Func, uses carbon nanotubes to disperse and functionalize the polycarbonate thermoplastic, enabling the creation of static-dissipative parts with advanced properties. This technology opens new possibilities for additive manufacturing in industries where ESD is critical in the production process or final product, as Mechnano’s PC ESD pellets offer consistent and precise ESD values.

Additive Industries, a 3D metal printer manufacturer, recently installed its MetalFABG2 3D printer at ADDDAM, an Italian supplier of volume flexible metal processing solutions. This marks Additive Industries’ entry into the Italian market, with ADDDAM using the MetalFABG2 to target the die-casting industry. The goal is to become a prominent producer of complex aluminum parts for the automotive and machine engineering sectors. With the automotive industry transitioning to electric vehicles, ADDDAM aims to offer prototyping and initial testing with the ability to scale up to high-pressure die-casting as electric vehicle volumes grow. The key factors driving ADDDAM’s decision to choose Additive Industries’ MetalFABG2 3D printer include its automation capabilities, cost-effectiveness, and high-quality production for die-cast replacement parts.
Snowbird Technologies has become Meltio’s sale partner, to offer Meltio’s technology as a standard component on the Snowbird Additive Mobile Manufacturing Technology platform (SAMM Tech). SAMM Tech is a patented additive manufacturing system housed inside a shipping container, designed for transportability and deployment to various locations worldwide. The integration of Meltio’s system, based on directed energy deposition (DED) process using wire as feedstock, allows SAMM Tech to efficiently produce large-format metal parts onsite and on demand. This solution caters to defense, aerospace, and energy sectors, enabling in-the-field production and equipment repairs.
Additionally, Alphacam has also become Meltio’s official sales partner. Alphacam will focus on building a supportive ecosystem for Meltio’s technology in the D-A-CH territory partnering and driving business opportunities alongside technology centers, tooling machine companies, robotic integrators, academia, and industry.
EOS North America‘s Additive Minds engineering group has launched the AM Turnkey consulting program, aiming to overcome obstacles associated with industrial 3D printing and streamline the AM production process. The program offers a Proof of Production guarantee on the customer’s own machine(s) upon completion. To facilitate AM Turnkey projects, EOS has established a dedicated, secure area at its Pflugerville, Texas technical center, where Additive Minds engineers and service technicians provide real-time management and support. Pilot customers have the option to collaborate directly with EOS, receiving detailed project mapping, 3D printer setup, ITAR-compliant machine bay, and full customer access to the purchased system for the project duration.
Florida-based company Custom Aerospace has recently become part of the Roboze 3D Parts Network. With over 30 years of industry experience, Custom Aerospace aims to enhance the accessibility of aerospace-certified additively manufactured components, providing performance comparable to metal components. The company adopts a multidisciplinary team approach, offering end-to-end component qualification and certification services, from concept to design and certification. By strategically joining the Roboze 3D Parts Network, Custom Aerospace plans to leverage advanced 3D printing solutions, particularly super polymer and composite additive parts, to deliver the benefits of additive manufacturing to its customers.
“Our inclusion in the Roboze 3D Parts Network signifies an essential step towards meeting the rigorous requirements of the aerospace industries. Through our partnership with Roboze, we can provide a wider range of certified components, thereby reducing lead times and increasing operational efficiency for our customers,” Evan Cramer, CEO of Custom Aerospace.
China-based Xi’an Bright Laser Technologies (BLT) has announced a record revenue growth of 66%, with sales totaling around US $140 million in 2022. The company expects this growth to continue in 2023. BLT is a leading provider of metal Additive Manufacturing machines and powders, catering to sectors like aviation, aerospace, energy, and medical industries. With ten machine models and prominent customers such as Airbus and HUAWEI, BLT recently launched its large-format BLT-S1000 Laser Beam Powder Bed Fusion (PBF-LB) Additive Manufacturing machine and expanded its powder production facilities.
Emerging partnerships from Oqton, FasTech, UPM Additive Solutions, Solukon, and more
Now proceeding with partnership news, Arkema has partnered with industrial 3D printer manufacturer Raplas to develop a range of high-performance N3xtDimension custom formulations for use in Raplas’ large format stereolithography (SLA) 3D printers. The collaboration will benefit from Arkema’s extensive material expertise for application-specific needs and new market trends.
These materials will be offered for use on Raplas Production Resin machines, which are open platform systems that enable shortened cycle time, high productivity, and large format prints with high resolution. The ready-to-print solutions will give end-users exceptional freedom of performance design to address varying application needs for investment casting, prototyping, and other demanding industrial applications. The collaboration will advance more sustainable production processes in the industry.
Next up, Artificial Intelligence (AI) software manufacturing company Oqton, has entered into a partnership with Castor. Bringing together the capabilities of these companies and their products provides manufacturers with a complete end-to-end solution for additive manufacturing — addressing the challenges faced by many when adopting and implementing the technology. The integration of Castor’s software with Oqton’s Manufacturing OS offers a seamless solution for manufacturing contractors and organizations to evaluate and analyze the business case and technical feasibility of using additive for manufacturing. An automatic, AI-driven system like this enables profitable growth for on-demand production.
Additionally, Oqton has also teamed up with Xact Metal, a powder bed fusion 3D printer manufacturer. Through this partnership, Oqton and Xact Metal are integrating their AM solutions to deliver automation and full process control at an affordable price. This will empower a breadth of users, from entry-level engineers to skilled experts, to realize the benefits of metal AM for R&D and production applications in a variety of industries.
Dr. Tushar Borkar from Cleveland State University (CSU) received a grant from Forging Industry Education and Research Foundation (FIERF) to investigate the use of AM processes to reduce the cycle time in forging operations. Dr. Borkar and Fastech Engineering (FasTech) are exploring wire arc additive manufacturing (WAAM) technology to manufacture forging preforms. FasTech’s WAAM system prints small to large-scale components in steel, titanium, nickel, and aluminum alloys at deposition rates of 5 kg/h in 3-and 5-axis configurations with advanced feedback controls. CSU will study processing parameters’ effect on microstructure and mechanical behavior of 316 stainless steel parts fabricated via WAAM and subsequent forging. Forged parts gain directional properties, enhancing strength, ductility, and resistance to impact and fatigue beyond AM alone. Results will be compared with vacuum hot press and spark plasma sintering. FasTech and CSU plan to expand this technology to manufacture other alloys for the forging industry, minimizing cycle time.

3D printing software developer Dyndrite and UPM Additive Solutions are collaborating to create “smart” metal build plates for the 3D metal printing industry. The build plate is an integral component in metal 3D printing. It lays the foundation for every part being built. Unfortunately, most users in the space do not record key data that can unlock the mystery around the lifecycle and history of their build plates. Without this information, for example, Laser Powder Bed Fusion (LPBF) users face an increased risk of powder leveling issues, internal fatigue, and plate warpage that can lead to lost time and costly build failures.
Dyndrite also announced that the first generation of VLM systems will be powered by Dyndrite’s software. The collaboration promises to boost productivity and automation for VLM users and provide software for unlocking manufacturing autonomy. This collaboration is yet another example of how machine builders are using the Dyndrite Application Development Kit (ADK) for the development of software applications to drive their machine hardware.
Depowdering company Solukon has partnered with Swiss firm URMA AG in the AM market. This collaboration expands Solukon’s global sales network and leverages URMA’s expertise in precision tool systems used for drilling. URMA offers a comprehensive approach to additive manufacturing, providing high-quality equipment through all process stages. They exclusively address automated depowdering with Solukon, renowned for its automated depowdering systems since 2015. Solukon’s Smart Powder Recuperation Technology SPR® ensures efficient removal of powder residue from complex metal parts. Together, Solukon and URMA will solidify their market position in Switzerland, benefiting from their combined strengths.
Celanese has announced a new strategic partnership between its Micromax Electronic Inks and Pastes and nScrypt, which designs and manufactures high-precision microdispensing and direct digital manufacturing (3D printing) equipment for various industrial applications. The collaboration aims to create innovative solutions across the printed electronics space through the extensive product portfolio of Micromax Electronic Inks and Pastes and the high-precision Factory in a Tool (FiT) line of manufacturing systems from nScrypt.
“We are energized about the possible new applications that can be developed through our partnership with Celanese,” said Ken Church, nScrypt founder and CEO. “By using our FiT technology and applying the Celanese Micromax advanced materials science, we now can formulate customized solutions with high-precision accuracy and flexibility.”
Essentium, an industrial additive manufacturing company, has partnered with 3D-Fuel, a leading functional 3D printing filament manufacturer, to simplify material procurement for 3D printing customers. This collaboration offers a comprehensive range of filaments from a single provider, with 3D-Fuel’s production now consolidated to Essentium’s certified Texas facilities for the North American market, ensuring efficient scaling and delivery of US-made materials. Customers gain access to both 3D-Fuel and Essentium portfolios, enhancing their experience. Additionally, 3D-Fuel’s partnership with NatureWorks, a PLA biopolymer manufacturer, supports the production of eco-friendly 3D printing materials, aiming to reduce the carbon footprint of the desktop 3D printing market.
Polish 3D printer manufacturer Zortrax and AM Centre of Excellence (AM-COE), have collaborated to create a dedicated 3D printer for demanding ceramic resins. Zortrax will be the manufacturer of this solution and will provide AM-COE with the printers. Together, Zortrax and AM-COE will develop and market the ActiveCera M, a professional 3D printer tailored for handling challenging ceramic resins. Zortrax brings its expertise in developing high-quality 3D printers, post-processing devices, a wide range of resins, and resin 3D printing software. On the other hand, AM-COE possesses professional research facilities and the capability to produce specialty resins. This partnership promises innovative advancements in the field of resin-based 3D printing.
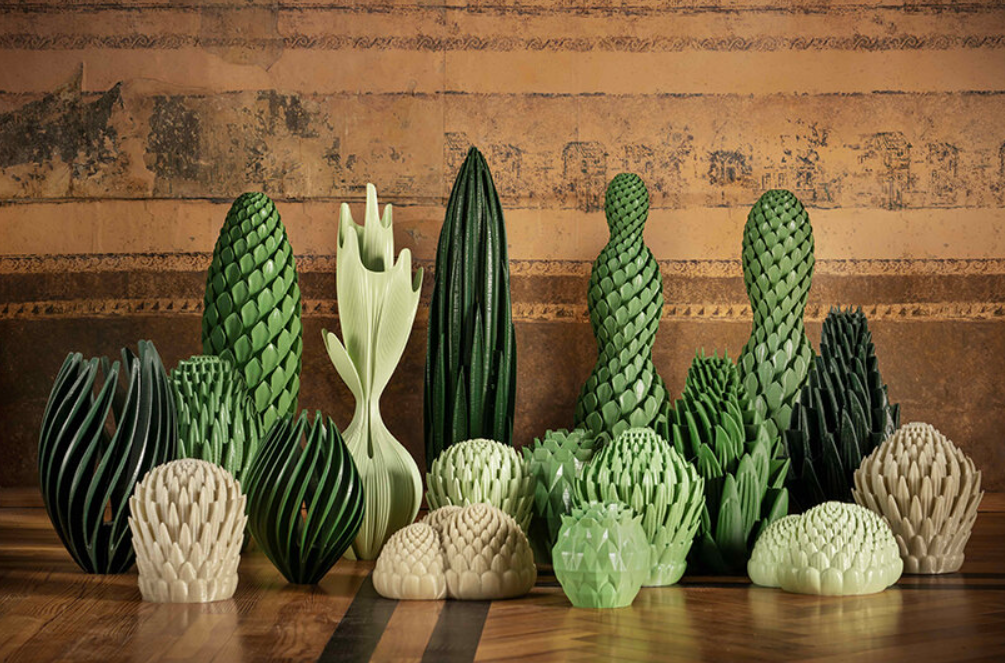
During Milan Design Week 2023, architecture studio External Reference collaborated with Barcelona-based practice LaMáquina to present their latest project, Pure Plants. The collection featured 3D-printed floral sculptures using an innovative material capable of purifying the air by absorbing CO2, nitrogen oxides (NOx), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Blending art, nature, and sustainability, the sculptures combined organic morphologies with new technologies, creating living representations of real plant species. Using Pure Tech technology and PLA, a bioplastic made from corn dextrose, the team successfully developed a 100% natural mineral compound that could help improve air quality both indoors and outdoors.

Metal AM technology company Velo3D has announced a strategic partnership with PhysicsX through Velo3D’s Technical Partner Program. The partnership gives Velo3D customers access to PhysicsX’s artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled physics simulation workflows to hyper-accelerate simulation loops, improve simulation fidelity, and algorithmically explore complex design spaces to unlock new performance levels. It also provides PhysicsX customers with access to the most advanced metal additive manufacturing capabilities available on the market today, so they can produce novel, highly optimized part designs with ease.
“We started working with PhysicsX when we were building the Sapphire XC printer because we needed to optimize the flow of gas in the printer build chamber to eliminate soot build-up around the laser windows of the system,” said Benny Buller, Velo3D Founder and CEO. “We quickly realized that PhysicsX’s capabilities could be a big boon to many of our customers who are pushing design performance limits. After working closely with them over the past two years, we’ve formalized our partnership to expose customers to the engineering synergy that exists by combining both companies’ technologies.”
nTop and EOS are collaborating on the development of Implicit Interop capability, aiming to address a significant bottleneck in the additive manufacturing (AM) workflow. The new nTop Implicit File allows for much smaller file sizes, up to 500 times faster file generation, and 60% faster load time, making complex designs more readily available for AM build preparation software. The technology was previewed at Formnext 2022 and received positive feedback from nTopology partners and customers. Siemens Energy showcased a proof-of-concept with an industrial heat exchanger, demonstrating the file’s efficiency in 3D printing. nTopology and EOS are also working with the 3MF Consortium to standardize the Implicit File format for broader adoption in the industry.
CMG Technologies has announced its collaboration with the US-based metal injection molding firm Indo-MIM group, “reflecting the dedication and expertise of its team in driving growth and success over the years.” The company will continue to operate as usual, maintaining our industry leadership in the UK, with Rachel Garrett and Dr Phil Marsh continuing to manage the company. With the support of Indo-MIM, CMG Technologies anticipate significant growth and investments in machinery and robotics to enhance our services.
AM solutions provider nano3Dprint has entered into a new strategic distribution partnership in Asia. Taiwanese firm Collimage International will be responsible for distributing nano3Dprint’s A2200 3D Multi-material Electronics 3D printer and B3300 Dual-Dispensing 3D printer to customers across Taiwan. Collimage International has already made sales to National Taiwan University, where undergraduate students in the photonics lab course will utilize the printers to design and print metallic electrode patterns for the development of self-powered solar devices. The partnership is expected to expand nano3Dprint’s presence in the region and facilitate the accessibility of their advanced 3D printing technologies.
South African 3D printing specialist Solid Edge Technology, and Swiss SLS 3D printer manufacturer Sintratec, have formed a partnership, making Solid Edge the first distributor of Sintratec in South Africa. Solid Edge Technology, with over three decades of experience in the 3D printing sector, specializes in design for Additive Manufacturing and production optimization. Previously using machines from another manufacturer, Solid Edge is now expanding its product range to include Sintratec’s SLS 3D printers. Sintratec offers modularity and scalability in its additive manufacturing solutions, providing customers in South Africa with a flexible entry into industrial 3D printing. This partnership opens new sales and service opportunities for Sintratec on the African continent.
“We are excited for the new possibilities that this partnership with Sintratec will allow us to explore within the South African additive manufacturing market. These technologies will bridge a required gap in the market, that currently is unfulfilled. Sintratec will complement our current product offering, perfectly,” said, Trevor Berry, Director and Owner, Solid Edge Technology.
The Chair of Microfluidics at the University of Rostock and Stenzel MIM Technik are collaborating on a 3D metal injection molding (MIM) tool project using AIM 3D‘s CEM technology with an Ex-AM 255 system. Funded by the German Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy, the project aims to create a near-contour cooling tool for metal injection molding. The 3D printing process allows the incorporation of helical channels directly into the tool, reducing cycle time by around 20%. The optimized 3D model is printed, sintered, and debound, resulting in complex metallic components rapidly. Stenzel MIM Technik anticipates up to 70-80% cycle time reduction.
New materials from Photocentric, Zortrax, Mechnano, Nanovia, and more
Followed by materials news, Photocentric introduces a new 50% plant-based resin to its materials library, featuring an oligomer derived from corn waste polyol. The 240 Bio-Based resin boasts high accuracy, tensile strength, and low water absorption, suitable for both daylight and UV printers, particularly for Photocentric’s LCD-based SLA 3D printers. Photocentric has explored various bio-based raw materials, including monomers from tree waste like camphene, known for inhibiting water uptake. As demand for sustainable 3D resins rises, the new generation of plant-based resins offers superior properties, eliminating the performance compromise users previously faced when opting for eco-friendly options.
Next up, Zortrax has introduced BASF Ultracur3D RG 3280, a ceramic-filled resin for the Zortrax Inkspire 2 3D printer, featuring superior hardness, high stiffness, and resistance to temperatures up to 280ºC. The resin’s stable particle dispersion and low viscosity ensure easy handling and 3D printing. Post-processing on Zortrax Cleaning Station and Curing Station produces ceramic-like features without the need for special furnaces. With a ready-made calibrated profile in Z-SUITE, users can easily process models, including rinsing and curing times. Post-processing in Zortrax Cleaning Station takes only 10-20 seconds, while Zortrax Curing Station takes about 30 minutes per side for each model.
Additionally, Zortrax’s Endureal industrial 3D printer is now compatible with BASF Ultrafuse PPSU filament, certified for use in the railway industry due to its flame-retardant properties. PPSU is resistant to extreme thermal conditions, fire, and chemicals, making it suitable for hydraulic and aerospace applications. The collaboration with BASF Forward AM expands the range of “advanced polymers” available for Endureal, which already includes ABS, ULTRAT, BASF Ultrafuse PC/ABS FR, metallic powder filaments, and high-performance polymers like PEEK, PEI, and PAEK. The Ultrafuse PPSU filament complies with the EN 45545-2 railway classification and UL 94 norm, offering V0 rating for minimizing fire spread risk in vehicles.
Mechnano has introduced its first Laser Sintering powder, “PK ESD,” utilizing its innovative D’Func technology (Discrete, Dispersed, and Functionalized Carbon Nanotubes). This new addition to Mechnano’s ESD material solutions for Additive Manufacturing is based on Jabil PK 5000 engineered powder combined with the D’Func-based formulation to introduce ESD properties to laser-sintered parts. PK ESD retains Jabil PK 5000’s advantages, including eco-friendliness, high-impact strength, chemical resistance, and improved elongation. Thanks to D’Func, PK ESD parts achieve Nano-Uniform ESD at 108 ohms surface resistivity while maintaining impressive mechanical performance, including a Flex Modulus of 988 MPa, UTS of 46 MPa, and Elongation at Break of 33%.
French 3D printing materials manufacturer Nanovia has introduced Flex B4C, a new semi-rigid filament enriched with boro carbide (B4C) for FDM/FFF 3D printers. The advanced composite material can absorb free neutrons and is suitable for 3D printing containers, fasteners, and components exposed to repeated vibrations in the nuclear and medical industries. Flex B4C is the second Nanovia filament dedicated to radiation control, following Nanovia PLA XRS for X-rays. With its ability to absorb free neutrons, Flex B4C offers an innovative solution for demanding applications in sectors that require advanced technologies and high-quality materials. The material is available in 1.75mm and 2.85mm diameters, priced at €490 per 500g spool.
Industrial 3D printing solutions provider Essentium has launched Essentium Altitude, known for its extreme cold resistance properties, and is now suitable for high-altitude applications like drones, outdoor housing, electrical line protections, and more. The material can be used on any open-source 3D printer, including Essentium’s High-Speed Extrusion (HSE) 180 and HSE 280i, enabling rapid production of cold-resistant parts on-demand. The material complies with Essentium’s certificate of conformance, offering individual spool traceability through the ISO and AS9100 quality process.
3D printing company Ultimaker introduces PET Carbon Fiber (CF) to its S series 3D printers‘ high-performance materials lineup. Ultimaker PET CF offers exceptional strength, high heat resistance, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for various industries. Engineers can create robust parts for manufacturing tools, fixtures, and end-use components, as well as conduct extensive testing of technical concepts with PET CF engineering prototypes. The material’s strength and thermal properties allow for swift production of replacement parts, reducing costly production line shutdowns. By annealing printed parts, temperature resistance of up to 181°C and increased strength and stiffness up to 30% and 10%, respectively, can be achieved, ensuring performance in challenging conditions.

Software launch and upgrades from Cubee, Materialise, General Lattice, and more
Glancing at the software news, first in line is GrabCAD Print version 1.80, released in July 2023, which introduces support for 2023 versions of CAD files, including Solidworks 2023, SolidEdge 2023, and Siemens NX 2212. The Print Pro feature allows users to add ad-hoc text labels to FDM parts with customizable size, depth, and spacing. Re-usable label templates can be created, embedding text, part names, and generating unique serial numbers. SAF nesting methods have been renamed to No Interlocks and Compact for better user understanding, with Compact now set as the default method. The VeroEcoFlex semi-flexible materials are now available for J850 TechStyle users, which utilize UV LEDs for accurate curing and UV LED Recipe control in GrabCAD Print. Various issues related to machine favorites, job estimations, and material settings for P3 users with OpenAM licenses have been addressed and fixed.
Cubee has introduced CubeeRecords, the world’s first “record label” for 3D printing designers, offering a comprehensive talent representation suite to maximize intellectual property monetization for 3D artists. As an extension of Cubee’s existing platform, which supports made-on-demand 3D printing businesses, CubeeRecords aims to represent and commercialize the works of 3D artists. They soft-launched “Hive,” a commercial licensing service, showcasing curated interior design collections from renowned designers such as Boem Brand, Gazzaladra Design, 3D Mini World, and more. Licensees gain access to not only STL files but also marketing assets, technical support, business advice, and a global peer community of business owners.
3D printing software and services provider Materialise is enhancing its Magics data and build preparation software with new features. The update prioritizes connectivity with other software solutions to establish a digital thread connecting the entire manufacturing process. Integration with CO-AM provides traceability by logging every action applied to a part or build, including user information. The update also includes integration with Materialise Machine Manager, facilitating the connection between users and Build Processors for successful builds. Moreover, Workflow Automation introduces its first off-the-shelf script, smart labeling, designed for Protolabs to automate repetitive workflows during data and build preparation. More Workflow Automation scripts will follow later this year.
Dimensionics Density, a division of Dimensionics GmbH in Germany, has launched a density determination system for additive manufacturing. The metrological system automates rapid and accurate density determination of components, aiding in the automation of AM part validation, particularly for critical end-use applications. The Dimensionics Density system conducts measurements automatically after samples are placed in universal component carriers, and it considers various environmental factors that can impact density measurements. The system uses the Archimedes Principle to achieve high accuracy by weighing the test object in different media. Deviations from the centre of mass are minimized, overcoming the limitations of manual Archimedes measurement solutions used in the industry.
General Lattice has unveiled its Digital Materials Platform – Frontier, in beta release, aiming to promote the adoption of additively manufactured applications and democratize the use of lattice structures. The platform treats lattice structures as traditional materials with tangible properties, providing a free-to-search library of validated mechanical property data to help users select the best lattice, material, and hardware combination. Users can access physical samples for hands-on evaluation, eliminating guesswork and saving time, money, and resources. Partnering with industry leaders like EOS, BASF Forward AM, and Photocentric, Frontier serves as a centralized source for validated Digital Material information, initially focusing on elastomeric polymers for foam replacement applications.
Neotech AMT and the University of Hamburg have collaborated on Project: KAM EI, a successful implementation of a camera-based monitoring system for 3D printed objects with integrated electronics. The project, funded by ZIM, aims to develop AI-driven quality assurance for additively manufactured objects. The Automated Quality Assurance (AQA) system, integrated into the 5-axis manufacturing cell, monitors and classifies the manufacturing process, automatically correcting processing errors. A vision system records the printed electrical structures, while image processing with AI checks for defects. This closed-loop system ensures precise conductive track printing, and the data are archived for certification support in critical applications.
Arkema and 3YOURMIND have launched the Easy3D material selection platform, combining Arkema’s material expertise and 3YOURMIND’s workflow. This platform allows customers to order parts with specific material specifications from Arkema’s advanced materials database, including thermoplastics, elastomers, and high-performance polymers. After uploading a 3D part file, the platform evaluates printability and suggests materials based on performance, fatigue resistance, and impact resistance. Users can compare materials, select qualified suppliers specializing in 3D printing technologies, and add parts to their order basket. Additional services like post-processing can be selected before submitting the order and payment.
Italian 3D printing company WASP has launched its WASP App, a slicing and parametric 3D modeling software aimed at enhancing the user experience with clay 3D printing. The app allows users to create custom design objects by manipulating parameters like shape, size, texture, and slicing settings. With the ability to export gcodes and print them directly using WASP’s Clay 3D printers, users can easily produce multiple pieces in series. Future updates will enable users to queue different gcodes in the same file, creating a range of unique pieces, aligning perfectly with WASP’s Clay Production System for automated customized piece production.

3D printing application news from Quintus Technology, ADDiTEC, and more
Quintus Technologies has introduced the Purus Toolbox to improve the production of critical parts, including medical implants, turbine blades, and rocket engine nozzles. The toolbox ensures unoxidized component surfaces after Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP), eliminating the need for costly pre- and post-processing methods. Oxidized surfaces, particularly alpha-cased titanium components, can lead to crack initiation, compromising component strength and reliability. The Purus Toolbox, consisting of HIP best practices, new equipment capabilities, and bespoke oxygen-getter cassettes, reduces these issues, offering design advantages and lowering manufacturing costs and environmental impact. The toolbox is now available as a retrofit for existing HIP systems or as a feature for new systems, with customers having access to the Quintus Care partnership program.
Metal AM company ADDiTEC has unveiled the Performance AMRC-P (Additive Manufacturing Robot Cell – Portable) at RAPID+TCT. This portable robotic system enables on-demand manufacturing with production-ready capabilities, eliminating long lead times associated with traditional methods. It supports printing of reactive metals like titanium and offers easy-to-use software tools for both novice and expert users. The system’s advanced features include a 6kW fiber laser configured deposition head, closed-loop process controls, and the ability to print large parts with intricate geometries using its multi-axis robotic architecture. ADDiTEC has partnered with major industrial robot brands for seamless integration, allowing for large-scale robotic 3D printing in a wide range of materials. Last year, ADDiTEC collaborated with Dr. Kuldeep Agarwal from Minnesota State University, Mankato, to enhance biocompatible bone implants using Ti-6Al-4V material.
Briggs Automotive Company (BAC) introduced the Mono R, an improved version of the world’s first road-legal, single-seater supercar. Achieving 0-62mph in 2.5 seconds, the Mono R showcases modern manufacturing techniques. As an early 3D printing adopter, BAC relies on UltiMaker’s ecosystem for fast and cost-effective production of customizable high-quality parts. Utilizing three UltiMaker S5 3D printers, BAC produces and tests multiple design iterations, optimizing performance, ergonomics, and aesthetics. The UltiMaker Digital Factory streamlines operations, ensuring consistency and repeatability while providing remote access for 24/7 on-demand production.
3D printer news from Chromatic 3D Materials, and Zortrax
Chromatic 3D Materials has expanded its RX-Flow 3D printer range with the new RX-Flow 2500, designed for printing thermoset polyurethane parts. The compact 3D printer offers a workspace of 348 x 543 x 194 mm and retains the cost efficiency, speed, and quality output of larger models. With a starting price of less than $30,000, the RX-Flow 2500 is suitable for manufacturers seeking to print durable, flexible parts at a low cost by eliminating the need for molds and reducing waste. The 3D printer’s technology minimizes material waste, saving some customers up to 90% in material costs compared to traditional production methods.
Zortrax launches a new speed mode feature for its M300 Dual and M Series Plus 3D printers, enabling up to three times faster printing without requiring any hardware changes. The free firmware upgrade enhances design flexibility, manufacturing capabilities, and shortens production times, making it ideal for businesses with critical lead times. Users can download the installation file from the Zortrax support center website and follow simple instructions to enable the speed mode. By adjusting print speed, acceleration, and hotend temperature offset, users gain more design flexibility, allowing some parts of a model to be printed at standard speed while accelerating others for quicker completion. The speed mode enhances production capacity and market competitiveness with faster order delivery times.
Certification news from Aerosport Additive, Ricoh USA, Thought3D, and more
Additive manufacturing company Aerosport Additive has recently obtained its ISO 9001:2015 certification. With over 25 years of experience in the field, the company has served numerous satisfied clients and remains dedicated to staying competitive in the market by continuously researching and investing in the latest technologies and processes. Geoff Combs, Founder of Aerosport Additive, expressed gratitude in the team’s efforts to achieve the certification, emphasizing the commitment to maintaining high-quality products and services for their customers. Looking ahead, the company aims for further growth and development in the industry.
Ricoh USA, Inc. has achieved FDA 510(k) clearance from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for its RICOH 3D for Healthcare, a HIPAA-compliant and ISO 13485-certified 3D medical manufacturing center. The clearance expands the capabilities of the center to include patient-specific anatomic modeling for diagnostic use in various medical fields, such as cardiovascular, neurological, gastrointestinal, genitourinary, and breast applications. The end-to-end workflow solution integrates with Merge Universal Viewer, making it easy to fit into existing hospital workflows. Ricoh’s centralized print-and-ship solution enables same-week delivery, while on-site production facilities offer next-day delivery for 3D-printed anatomic models, empowering healthcare providers with efficient and accurate diagnostic tools.
Additive manufacturing R&D company Thought3D has announced the attainment of CE, FCC, UKCA, and ISED certifications for its advanced 3D printing quality assurance tool, Drywise. These certifications validate the tool’s quality, safety, and reliability, opening up new global market opportunities. Additionally, Thought3D has established partnerships with resellers and distributors in regions like the US, Germany, Spain, Netherlands, Turkey, UK, and Southeast Asia, aiming to broaden the reach of its high-quality products. Drywise effectively addresses hygroscopicity issues for nylons and offers generic profiles for PLA, ABS, PETG, and specific TPU materials, streamlining the printing process and ensuring consistent, dependable results.
Rosswag Engineering has received TÜV SÜD certification for additive manufacturing of components made of 1.4404 (316L) according to the European Pressure Equipment Directive (PED) 2014/68/EU. The certification program ensures compliance with legal requirements for pressure equipment. Rosswag Engineering completed extensive testing and certification on the SLM®280 2.0 LPBF machine, guaranteeing the quality and reproducibility of additively manufactured pressure equipment.
“We want to offer solutions to transfer more functional optimized and additive manufactured components into industrial applications. But to be able to apply innovative heat exchangers, for example, there was no alternative to certification according to the Pressure Equipment Directive,” said Gregor Graf, Head of Engineering at Rosswag GmbH.
New research in the additive manufacturing sector
Researchers at Lancaster University have achieved a breakthrough by directly 3D printing conducting polymer structures inside a living organism. The process, though in its early stages, has the potential to create next-generation implants for real-time health monitoring and medical interventions like neuromodulation. Led by materials scientist John Hardy, the team used a high-resolution fast pulsed laser 3D printer to create conductive volume pixels (Voxels) within the organism, specifically nematode worms. The success of this additive process opens possibilities for human-computer interfaces and more complex circuits in the future, but ethical considerations will also be addressed in further research.
“We needed to make sure that the precursor monomer mixture was biocompatible, which is more difficult than once the material is polymerised and ‘inert’, and that the light used to polymerise the monomer does not harm the animals by burning surrounding tissue. This was possible because we used lower energy lasers and a ‘two-photon’ set up,” says the research collaborator Alexandre Benedetto.
Barson Corporation subsidiary Himed has conducted research on surface finishing for titanium and titanium-alloy implants. They developed the micro-abrasive material known as MCD Apatitic Abrasive, which is used for post-processing 3D-printed implants. The research highlights the benefits of using this biocompatible abrasive to achieve a uniform surface texture on the implants for successful osseointegration. Himed has been working on this technology for nearly 30 years and has refined its application for various orthopedic and dental implant designs. The company’s proprietary MATRIX MCD process has shown positive results in improving implant surfaces while eliminating residual contaminants that may inhibit biological fixation or shed in vivo.
Law and regulatory news from Markforged and Chemical Insights Research Institute
Industrial additive manufacturing company Markforged received a notification from Nasdaq (NYSE) stating that the company is not in compliance with the minimum average closing price requirement over a consecutive 30 trading-day period. However, it’s important to note that this notice does not mean an immediate delisting of the company’s common stock from the NYSE. Markforged intended to inform the NYSE of its intent to regain compliance within 10 business days and has a six-month cure period during which it can regain compliance at any time.
The Chemical Insights Research Institute (CIRI) of UL Research Institutes, along with standard stakeholders, has updated the consensus standard (ANSI/CAN/UL 2904) for testing and assessing particle and chemical emissions from 3D printers. The update includes the addition of two new chemicals, tetrahydrofuran (THF) and tetradecamethylcycloheptasiloxane (TDMCHS or D7), to the list of chemicals with required emissions criteria from operating 3D printers. THF is a possible human carcinogen, and TDMCHS is frequently emitted from 3D printers, contributing to the total Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) emission level. The Standard applies to consumer-level material extrusion 3D printers commonly found in non-industrial indoor spaces. These emissions can impact indoor air quality and may have adverse health effects, particularly for vulnerable individuals with respiratory or cardiovascular conditions. The standard updates clarify definitions, update print object instructions, and add new VOCs while removing others from the allowable emissions criteria list.
L3Harris tests 3D printed satellite components on ISS
L3Harris Technologies is conducting a project on the International Space Station (ISS) National Laboratory to test 3D printed satellite components. The experiment aims to assess the durability of the 3D printed radio frequency circuit and various material samples in the harsh environment of low Earth orbit (LEO). The project also includes testing photonic material for photonic integrated circuits used in satellite communications. Eduardo Rojas and students from Embry Riddle Aeronautical University are assisting with the investigation, which will utilize the MISSE Flight Facility on the exterior of the ISS. The results will be used to incorporate the materials into satellite manufacturing and explore other space-based applications for 3D printed materials.
“We’re excited to test the 3D printed materials for six months and compare the new results with previous ISS experiments and ground tests,” said Arthur C. Paolella, senior scientist and technical fellow with L3Harris, an aerospace and defense industry leader. “The ability to 3D print materials for use in space opens up new possibilities for satellite design and construction while making spacecraft manufacturing more cost-effective and efficient.”
Awards obtained in the 3D printing sector
The Applied Science & Technology Research Organization of America (ASTRO America) has announced the winners of its first major sub-award under the Other Transaction Agreement (OTA) to develop additive and advanced manufacturing technologies for the U.S. Army. Boeing, General Dynamics, Corvid & BAE Systems team, and Virginia Tech & John Deere team will receive awards totaling over $1.5 million. They will demonstrate the effectiveness of the world’s largest metal 3D printer in developing parts for their supply chains. The goal is to modernize manufacturing processes, reduce weapon systems’ cost and delivery time, and support the warfighter. ASTRO America will continue to offer workshops, industry days, and funding opportunities under the OTA.
Four UK engineering innovators will be honored with The Princess Royal Silver Medal, a prestigious award from the Royal Academy of Engineering. Joel Gibbard MBE, CEO of Open Bionics and Samantha Payne MBE, COO of Open Bionics will receive the medals at the Academy Awards Dinner. Their notable contributions involve advancements in prostheses, blockchain applications for pediatric care in warzones, and cybersecurity and biometrics. Additionally, Open Bionics, utilizing 3D printing for accessible bionic arms for children, and mOm Incubators, creating portable neonatal incubators for NHS hospitals and war-torn regions, will be recognized for their exceptional work.
Formnext 2023 to highlight sustainability in AM with Nordic partner country
Formnext 2023, set for 7 – 10 November, will feature the Nordic region as its partner country, including Denmark, Finland, Norway, and Sweden. Alongside the innovative Nordic companies participating in the leading exhibition for AM technologies, they will emphasize sustainability, focusing on energy and material efficiency. The Nordic pavilion will host around two dozen exhibitors showcasing successful AM applications. Supporting events will highlight inspiring AM use cases, with the Danish AM Hub leading a panel on sustainability. Diverse manufacturers from the region, including well-known companies like Lego and Sandvik, will present their innovations, showcasing how the Nordic region leads in responsible and sustainable manufacturing.

What does the future of 3D printing for the next ten years hold?
What engineering challenges will need to be tackled in the additive manufacturing sector in the coming decade?
To stay up to date with the latest 3D printing news, don’t forget to subscribe to the 3D Printing Industry newsletter or follow us on Twitter, or like our page on Facebook.
While you’re here, why not subscribe to our Youtube channel? Featuring discussion, debriefs, video shorts, and webinar replays.
Are you looking for a job in the additive manufacturing industry? Visit 3D Printing Jobs for a selection of roles in the industry.
Featured image shows Pure plants collection. Image via LaMáquina.



