Standards help facilitate communication between geographical communities and within businesses. As a relatively new industry, there is an overwhelming need for standards development in 3D printing, not only to ensure the safety of process, but also to improve efficiency, strengthen interactions, more easily exchange equipment and broaden the technology’s capabilities.
There are currently standards in place for various manufacturing technologies, from established methods like CNC machining and injection molding, to some select 3D printing modalities relevant to aerospace and medical industries. As each of these technologies work together on the shop floor, it is important to link these standards together, collecting all the data in one place to help optimize production. With optimization comes an inherent potential for automation. This feature is necessary for the realization of 3D printing in production.
German 3D printing software developer 3YOURMIND is seeking to create a solution to standardize the way these multiple different datasets are collected. Already, the company has begun working with DIN, the German Institute for Standardization, America Makes and the Universal Machine Tool Interface (umati) standardization group to achieve this goal. Together, they are collaborating to create a technical communication standard for machine connectivity in 3YOURMIND’s additive manufacturing workflow.
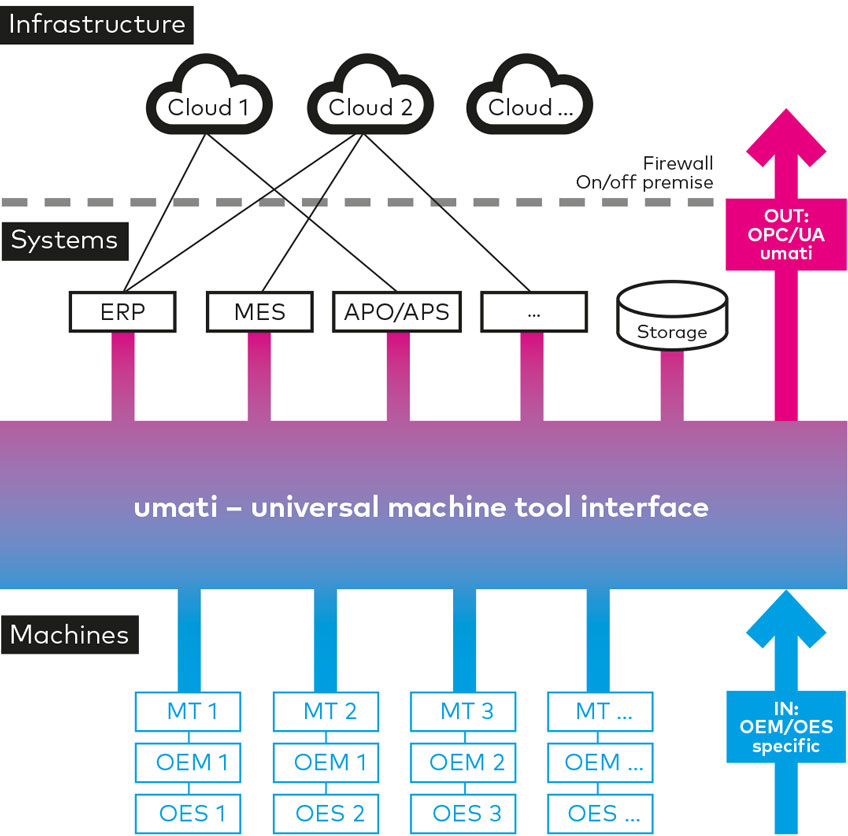
The Universal Machine Tool Interface
Launched in 2017 by the German Machine Tool Builders’ Association (VDW), umati aims to establish a worldwide standard for simple data transfer between various tooling machines, which includes 3D printing systems and production management software. It enables machine tools and peripherals to connect to customer-specific IT ecosystems.
Upon launch of the project, major machine tool builders such as Trumpf and DMG Mori committed themselves to the umati working group. As work continues on developing the standard, VDW also announced the addition of CNC control manufacturers B&R Automation and Mitsubishi Electric to the group as well, in early 2019. At EMO Hannover 2019, a demonstration of umati interface standard use cases took place, with numerous machines and controls connected to the umati demo dashboard.
How to automate the entire additive manufacturing workflow?
3YOURMIND software for streamlining and automating production on the factory floor has already been used for a few years in their order Management solution. Last year, 3YOURMIND launched its Agile Manufacturing Execution System (Agile MES) product, a program that automates part and job scheduling to ensure that projects meet deadlines, and give users the power to quickly identify any setbacks or areas of improvement. Such software is becoming standard on the market, despite healthy competition in this field.
With these processes, companies have been able to standardize the 3D printed production on a part by part basis. But as Stephan Kühr, CEO of 3YOURMIND, explains, this is not enough, “By making production data visible within our software, we are providing an important tool to automate processes. Most importantly, since most production halls are running machines from different vendors, the Agile MES is a system where all that data can be compared and stored together. For engineers this is a huge advantage for keeping an overview of production.”
Aside from 3D printing parts in the machines, the majority of the remaining additive manufacturing processes, between each system, are still manual, from scheduling, to sorting data, to tracking production on paper travellers for auditing. Furthermore, post-processing technology is either manually operated, or uses separate data standards.
Digitizing the entire production chain, from powder preparation, to post-production to quality control, is therefore key for automation. Standardizing data for additive manufacturing machines, post-processing systems and other manufacturing technologies in a single format allows for the creation of auditable trails that can be tracked digitally, essential for quality assurance. Kühr adds, “By standardizing that data, we create reference points so that in the near future they can certify processes for groups or types of parts. And ideally repeat those production steps around the world.”
![Diagram explaining 3YOURMIND’s approach towards creating data standards for machine connectivity. Image via 3YOURMIND.]](https://3dprintingindustry.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/agile-mes_machine-connectivity-01.png)
Establishing data connectivity standards between machines
3YOURMIND joined the umati working group in August 2019 alongside leading machine vendors, and is operating as the main software participant in the group’s work to employ the umati standard for the additive manufacturing process chain. The aim is to establish a standard for reading and sending data between software systems and production machines. This will help enable automation and increase access to serial additive manufacturing for the whole industry.
The umati standard was chosen by 3YOURMIND as it is specifically designed to function with virtually all modern, automated production and post-processing machines. It is based on OPC UA, an open machine to machine communication protocol, therefore allowing devices across different industrial sectors to connect on one platform. A cross-technology approach is important to enable connectivity between different technologies. “Our work on machine connectivity is based on the umati standard,” explains Andres Repcik, Product Manager for Machine Connectivity at 3YOURMIND. “It is being actively developed for data transfer speed, includes sending data based on the OPC/UA read-write capabilities and is a full dictionary that unites AM machines, tooling systems and software applications,”
3YOURMIND is also discussing the overall standards with America Makes, the national accelerator for additive manufacturing. America Makes has an ongoing initiative with the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) aiming to accelerate the development of industry-wide additive manufacturing standards.
From those discussions, it became clear that MTConnect must also be part of the machine connectivity data standard 3YOURMIND creates. The goal is to unite the industry, instead of causing division by creating separate data standards. Part of this task involves translating all data information types, including data from MTConnect, UPC/UA and machine-specific API connections, into a single standardized interface instead of trying to force adoption of another standard. Repcik adds:
“We know how important it is to work with the status quo so we will accept data from MTConnect or custom machine APIs (Application Program Interfaces) and format the data to umati for processing. This communication framework is a critical milestone on the way to Agile Manufacturing.”

Find out more about 3YOURMIND’s Machine Connectivity at formnext, at Booth E61, Hall 11.1.
Subscribe to the 3D Printing Industry newsletter for the latest news in additive manufacturing. You can also stay connected by following us on Twitter and liking us on Facebook.
Looking for a career in additive manufacturing? Visit 3D Printing Jobs for a selection of roles in the industry.
Featured image shows diagram explaining 3YOURMIND’s approach towards creating data standards for machine connectivity. Image via 3YOURMIND.


