The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) released ISO 5425:2023 in August 2023. This new standard is titled “Specifications for the use of Poly(lactic acid) (PLA)-based filament in additive manufacturing applications.”
By defining technical specifications and guidelines, the ISO 5425:2023 standard ensures the consistent and quality-controlled utilization of PLA filament in 3D printing applications within the industry. The process leading to the publication of this standard began in September 2019 when Shenzhen-based company, Esun Industrial Co., Ltd. (aka eSUN) and Beijing Technology and Business University jointly introduced a new work item proposal (NWIP) at the ISO/TC 61 annual meeting. Following its acceptance, a dedicated working group comprising global experts convened for numerous meetings to plan and develop this standard.
“The publication of ISO 5425:2023 signifies a pivotal milestone that will bring much-needed structure and order to the realm of 3D printing technology. This standard is poised to play a pivotal role in the expansion and proliferation of 3D printing technology worldwide, fostering innovation and quality in the industry,” said eSUN.
A comprehensive framework for PLA filament
Notably, the standard underwent a rigorous consultation and approval process, which involved several voting stages, including Working Draft (WD), Committee Draft (CD), and Draft International Standard (DIS). What is particularly notable is that the standard successfully resolved significant issues early on, resulting in a seamless progression through the approval process, with no technical comments raised during the DIS balloting phase. Consequently, the Final Draft International Standard (FDIS) stages were bypassed, and the ISO published the standard.
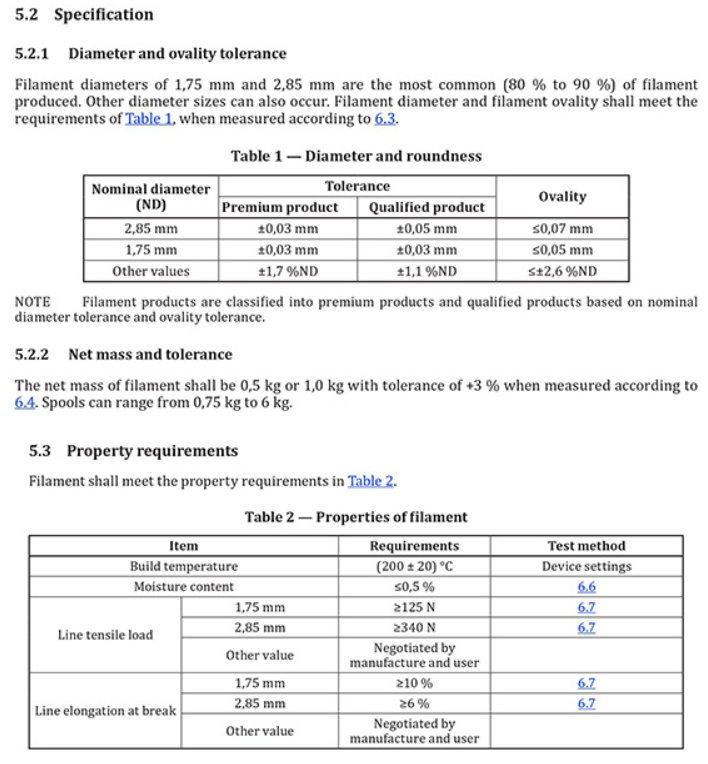
ISO 5425:2023 is a vital document that describes the technical specifications for PLA filament, encompassing essential parameters such as appearance, net mass and tolerance, diameter, ovality tolerance, volatile matter limits, line tensile load, and line elongation at break. In addition to these specifications, the standard provides a framework for test methods, detection rules, marking, labeling, packaging, transportation, and storage of PLA filament.

Use of PLA in 3D printing over the years
PLA, a bio-based polymer produced using lactic acid from the sugar fermentation process, was initially conceived as a greener substitute for petroleum-based counterparts. While technically biodegradable, it requires industrial composting conditions. Beyond its role as the primary polymer in desktop 3D printing, PLA finds use in various sectors, including packaging and disposable cups.
eSUN was established in 2002 and is mainly engaged in PLA polymerization, modification, application, and recycling. In 2007, eSUN launched commercial PLA filaments. Its PLA+ is widely praised for its ease of printing, high performance, and stability. In 2022, eSUN launched a series of high-speed printing materials.
This year, Filamentive, a UK-based 3D printing filament manufacturer, unveiled its newest offering, Economy PLA. Featuring a substantial blend of nearly 99.99% recycled components, this PLA filament positions itself as a potentially environmentally friendly choice in the 3D printing filament sector, says the company. Additionally, Economy PLA is available in black and white variants.
Last year, Canadian 3D printing materials start-up Fortis3D distinguished itself in the filament market with three product lines – Essential, Advanced, and Industrial – for hobbyists, professionals, and industry. These product lines involve custom PLA filament formulations and compounding, enabling novel resin modifications. Notable offerings included BioDuro PLA, uniting toughness with mechanical strength, and BioDuro Metallic PLA with metallic and iridescent effects. Pilates PLA, a plasticizer-free flexible filament, and Lignum PLA, a 25% wood-filled option, rounded out the product range. These filaments are available in 1.75mm formats, with 2.85mm options.
Who will win the 2023 3D Printing Industry Awards? Make your nominations now!
What does the future of 3D printing for the next ten years hold?
What engineering challenges will need to be tackled in the additive manufacturing sector in the coming decade?
To stay up to date with the latest 3D printing news, don’t forget to subscribe to the 3D Printing Industry newsletter or follow us on Twitter, or like our page on Facebook.
While you’re here, why not subscribe to our Youtube channel? Featuring discussion, debriefs, video shorts, and webinar replays.
Are you looking for a job in the additive manufacturing industry? Visit 3D Printing Jobs for a selection of roles in the industry.
Featured image shows eSUN’s latest engineering filament- Carbon Fiber PLA (ePLA-CF). Photo via eSUN.



