Following the appointment of a new CEO, 3D printing service provider Materialise has introduced the CO-AM Quality & Process Control (QPC) software to enhance the adoption of additive manufacturing for volume production.
This system enables comprehensive quality monitoring and data analysis throughout the manufacturing process. To streamline customer services and order management, Materialise has collaborated with DigiFabster, a quoting automation and e-commerce solution. Additionally, Materialise has partnered with Ansys to simplify simulation for 3D printing. Materialise is presenting these innovations at Formnext 2023 this week at booth C139 in hall 12.1.
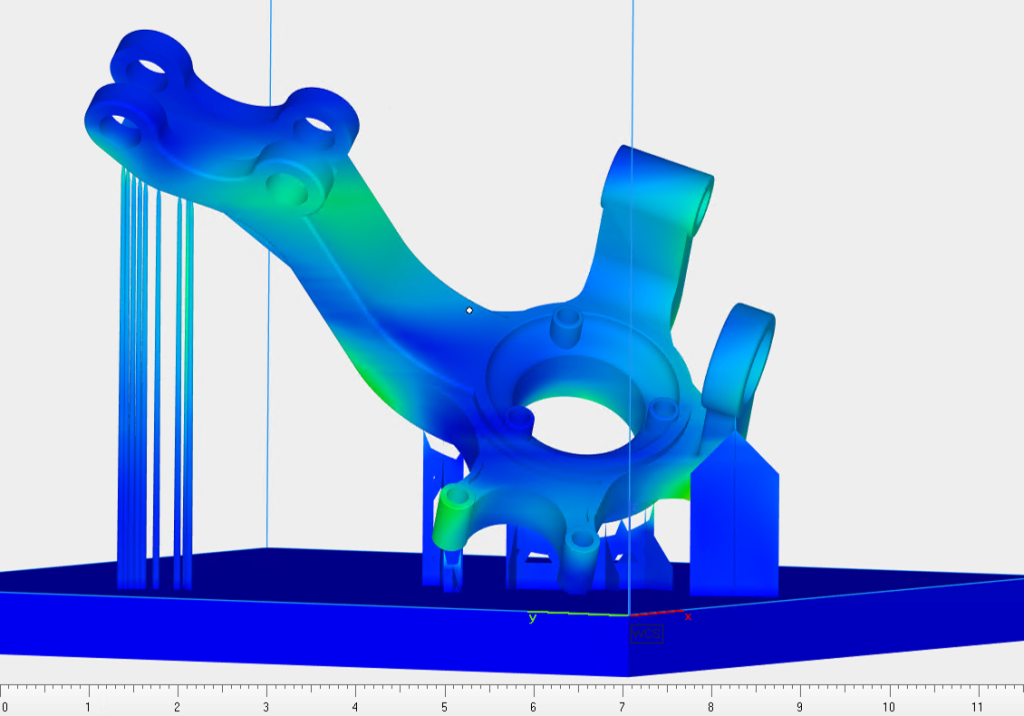
“Usability and performance are crucial when it comes to simulation,” explained Chris Robinson, Senior Product Manager, Ansys. “By integrating Ansys technology into Materialise’s comprehensive software solutions, AM users can benefit from a seamless workflow using the gold standard in simulation.”

Enhancing quality control and streamlining order processing for 3D printing
The QPC system enables comprehensive monitoring and analysis of vital part quality data throughout the production process. It covers essential data sources like 3D models, raw materials, process parameters, in-situ monitoring, post-processing, and quality inspection. Manufacturers can use it at various product development stages, offering a holistic view of their processes. Materialise introduced the QPC Layer Analysis module earlier this year, which has since expanded to include more in-situ monitoring data sources and CT scan correlation. The QPC Process Lab module encourages team collaboration, streamlining data centralization for accelerated product development and seamless research-to-production monitoring.
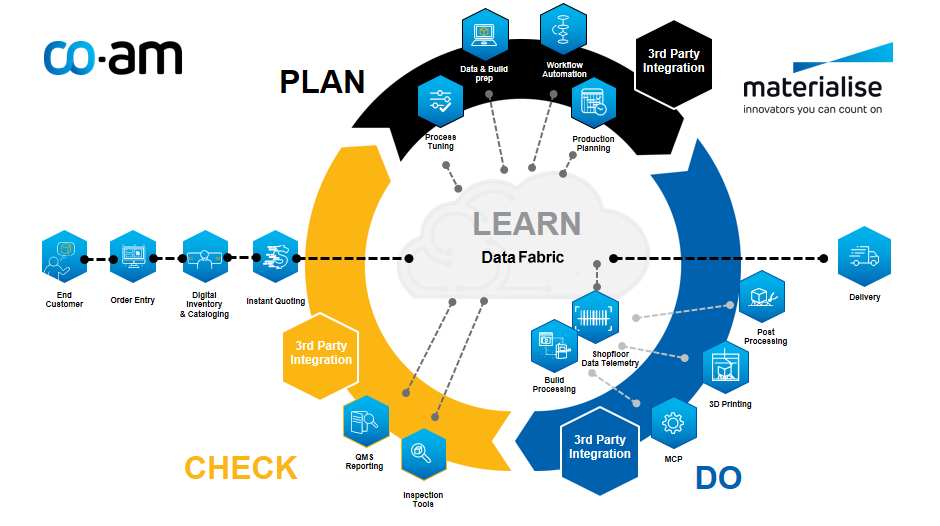
The QPC system is a key part of Materialise’s CO-AM software platform, offering a comprehensive suite of tools for 3D printing. It provides access to solutions from Materialise and third-party partners, covering design automation, mass customization, automated labeling, and post-processing. Users can efficiently manage diverse technologies. Materialise recognized the demand for quick 3D printing services. Traditional order processing via phone and email, often with scattered data, can raise administrative costs. This led to Materialise partnering with DigiFabster aiming to tackle these challenges.
Partnerships to enhance digital manufacturing workflow
DigiFabster’s eCommerce, automated quoting, and payment solutions will integrate smoothly with Materialise’s CO-AM software platform. The white-labeled eCommerce portal employs machine learning to automate quoting, saving manufacturers time and costs. This integration ensures 24/7 quoting availability for customers. Additionally, it streamlines order management within CO-AM’s Order Management System, enhancing order tracking and offering immediate status updates to customers.
“Speed and reliability are essential for manufacturing companies,” says Const Ivanov, CEO of DigiFabster. “Working with Materialise, we will be able to offer a digital manufacturing workflow that offers a modern customer experience and helps users get paid on time. This partnership will offer significant value to our customers.”
Materialise has partnered with Ansys to optimize 3D printing simulation. This collaboration simplifies simulation for Materialise Magics users, enhancing accessibility and cost-effectiveness. Ansys’ Additive Suite technology seamlessly integrates into Materialise’s Magics software, streamlining the workflow and reducing complexity in applying simulation results during build preparation. The ongoing partnership between Materialise and Ansys aims to uncover additional avenues for enhancing AM process simulation.
Materialise spearheads 3D printing advancements for mass production and beyond
Materialise aims to advance 3D printing for volume production and will be showcasing successful cases presented at Formnext, spanning industries like medical technology, automotive, and aerospace. Notable examples include biotech firm Sartorius, which utilized 3D printing for biocompatible plastic part production, resulting in design enhancements and a faster time-to-market. CMB.TECH, specializing in large-scale marine and industrial solutions, partnered with Materialise for 3D printed components for its hydrogen-diesel hybrid technology, streamlining manufacturing processes.
“Everything from machining to the assembly process is much simpler when you can remove the complexity in the build phase by using AM. Materialise takes care of all of it, so we receive a fully finished part,” said Roy Campe, Chief Technology Officer of CMB.TECH.
Materialise’s interests extend beyond 3D printing for mass production; it is also showcasing novel post-processing technology, says the company. The Continuous Fibre Injection Process (CFIP), created by Reinforce3D, strengthens 3D printed parts. It does so by injecting continuous fibers, like carbon fibers, with resin, allowing these fibers to penetrate deep within hollowed sections. After curing, this process significantly bolsters the structure’s strength, providing exceptional mechanical performance and reduced weight.
Voting has now started for the 3D Printing Industry Awards 2023. Cast your vote now!
What does the future of 3D printing for the next ten years hold?
What engineering challenges will need to be tackled in the additive manufacturing sector in the coming decade?
To stay up to date with the latest 3D printing news, don’t forget to subscribe to the 3D Printing Industry newsletter or follow us on Twitter, or like our page on Facebook.
While you’re here, why not subscribe to our Youtube channel? Featuring discussion, debriefs, video shorts, and webinar replays.
Are you looking for a job in the additive manufacturing industry? Visit 3D Printing Jobs for a selection of roles in the industry.
Featured image shows Materialise, DigiFabster, and Ansys partner to drive 3D printing innovation. Photo via Materialise.



