Siemens, Europe’s largest industrial manufacturing company, has signed an agreement to acquire Atlas 3D, the cloud-based developer of Sunata, a print preparation software for Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) 3D printers.
The acquisition is to be made by Siemens Digital Industries Software, formerly Siemens PLM, which specializes in automation and digitalization, and seeks to decrease 3D printing errors caused by thermal distortion. Zvi Feuer, Senior Vice President, Manufacturing Engineering Software of Siemens Digital Industries Software, stated:
“We welcome Atlas 3D to the Siemens community as the newest member of our additive manufacturing team. Our solutions industrialize additive manufacturing for large enterprises, 3D printing service bureaus, design firms, and CAD designers,”
“The cloud-based Sunata software makes it easy for designers to determine the optimal way to 3D print parts for high quality and repeatability. The combination of Sunata with the robust CAE additive manufacturing tools in Simcenter enables a ‘right-first-time’ approach for industrial 3D printing.”
Sunata under Siemens Digital Industries
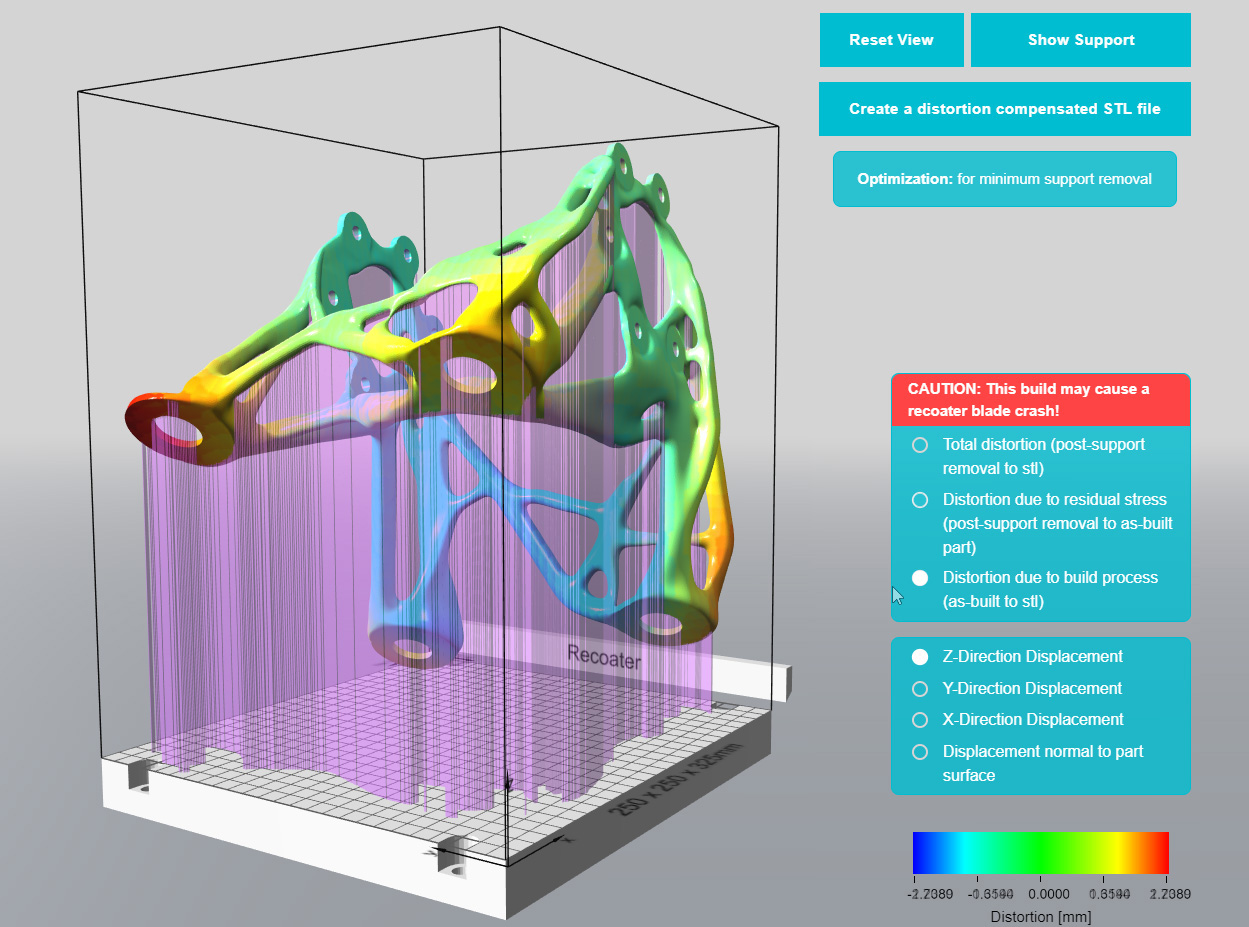
Headquartered in Plymouth, Indiana, Atlas 3D’s additive manufacturing software Sunata was released in 2018, and addresses the rate of 3D print failures within high-volume production. According to the company, factors such as part orientation, distortion, and heat extraction uniformity are often neglected as a result of numerous design iterations across the production process.
Using patent-pending Thermal Circuit Network (TCN) technology, Sunata improves the simulation process to optimize additive manufacturing. It automatically optimizes part build orientation and generates support structures, allowing a designer to avoid failures.
Intending to decrease downstream analysis, Sunata will be integrated into Siemens’ Simcenter software, which simulates the powder-based laser application process to enable ‘first time right’ prints. This will be accessible online through Siemens’ Additive Manufacturing Network, a collaborative platform cultivating on-demand design and engineering expertise, digital tools and production capacity.
Siemens and Industry 4.0
Siemens Digital Industries Software has previously partnered with U.K. universities for the Connected Curriculum, which aims to bring advanced industrial tools, data, and approaches into the universities’ respective apprenticeship, undergraduate and master courses. It is also a partner in Germany’s Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) grant project Industrial implementation of digital engineering and additive manufacturing (IDEA).
Referring to the Atlas 3D acquisition, company CEO Chad Barden, added, “Siemens is a leader in additive manufacturing, with the most integrated and functionally robust solutions in the industry, so we are excited to join the team. The power of Sunata is that it equips designers to more easily design parts that are printable, which helps companies more quickly realize the benefits of additive manufacturing.”
“As part of Siemens, we look forward to introducing Sunata to customers who already have Siemens’ AM solutions and can achieve new efficiencies in their front-end design-for-additive process, as well as companies who have yet to start their additive manufacturing journey.”
The acquisition is due to close at the end of November 2019. The terms of the transaction have not been disclosed.

Don’t forget to subscribe to the 3D Printing Industry newsletter and follow us on Facebook and Twitter.
Looking for your next additive manufacturing career move or searching for new talent to join your team? Visit our 3D Printing Jobs site now.
Featured image shows insights into the optimal part build orientation in order to minimize supports, distortion, effort to remove supports, part material, and printing time. Image via Atlas 3D.

