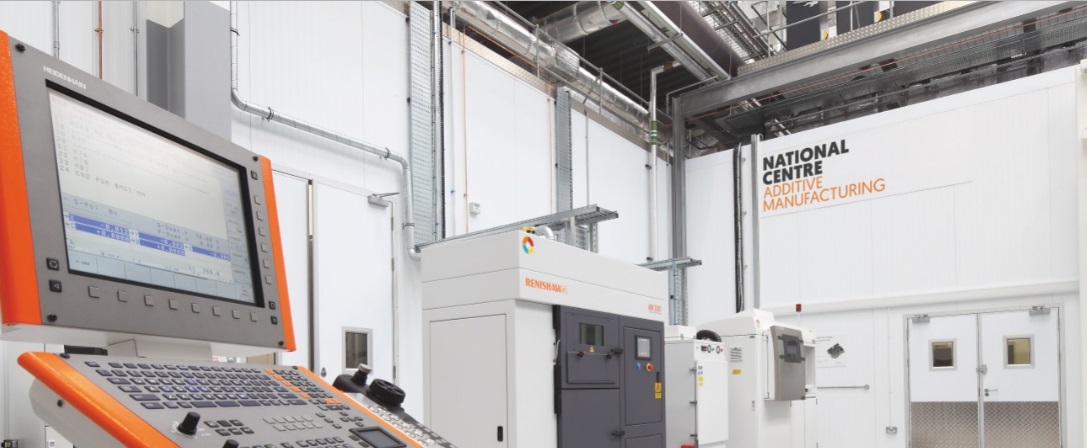
The National Centre for Additive Manufacturing (NCAM), based at the Manufacturing Technology Centre (MTC) in the UK, has launched a project to facilitate greater adoption of 3D printing in highly regulated sectors such as aerospace, space, oil and gas, and medical.
Funded by UK Research and Innovation through the Industrial Strategy Challenge Fund, the Daedalus project aims to add value to the UK’s 3D printing landscape by producing a framework for capturing and managing data throughout the entire additive manufacturing supply chain.
“We are really excited to start work on the Daedalus project,” said Alex Morrison, Advanced Research Engineer at NCAM. “As part of the project consortium, we can add significant value to the UK additive manufacturing community by demonstrating a digital thread running through a highly regulated AM supply chain.”

HiETA, Arrowsmith, and Valuechain join Daedalus
Joining NCAM for project Daedalus is Bristol-based metal additive manufacturing technology developer HiETA Technologies, which will be leading the project, alongside precision engineering firm Arrowsmith Engineering in Coventry, and global enterprise software business Valuechain Enterprises.
The partners are currently six months into the project’s two-year program, which will conclude in July 2022. Working with the MTC and NCAM, they will each contribute their specialist knowledge and capabilities to the project throughout its duration.
“We want to support UK manufacturing getting into additive, and producing quality parts to supply highly-regulated industries,” Morrison continued. “During the project, we will produce a framework for capturing and managing data throughout the entire AM supply chain – the end-to-end digital thread. We will show the benefits of that system in demonstrators at the NCAM, Arrowsmith, and Valuechain.
“These benefits include using that digital thread data to power new analytics like our AI solutions to drive higher-quality parts at lower costs.”
HiETA brings traceability, part quality, and AI
Tasked with coordinating the consortium over the next 18 months, HiETA brings extensive experience in additive design and production across a range of highly-regulated sectors. Throughout the project, the company will be showing how an additive manufacturing supply chain member can connect to the digital thread, and how doing so can deliver traceability, flexibility, and part quality for their customers.
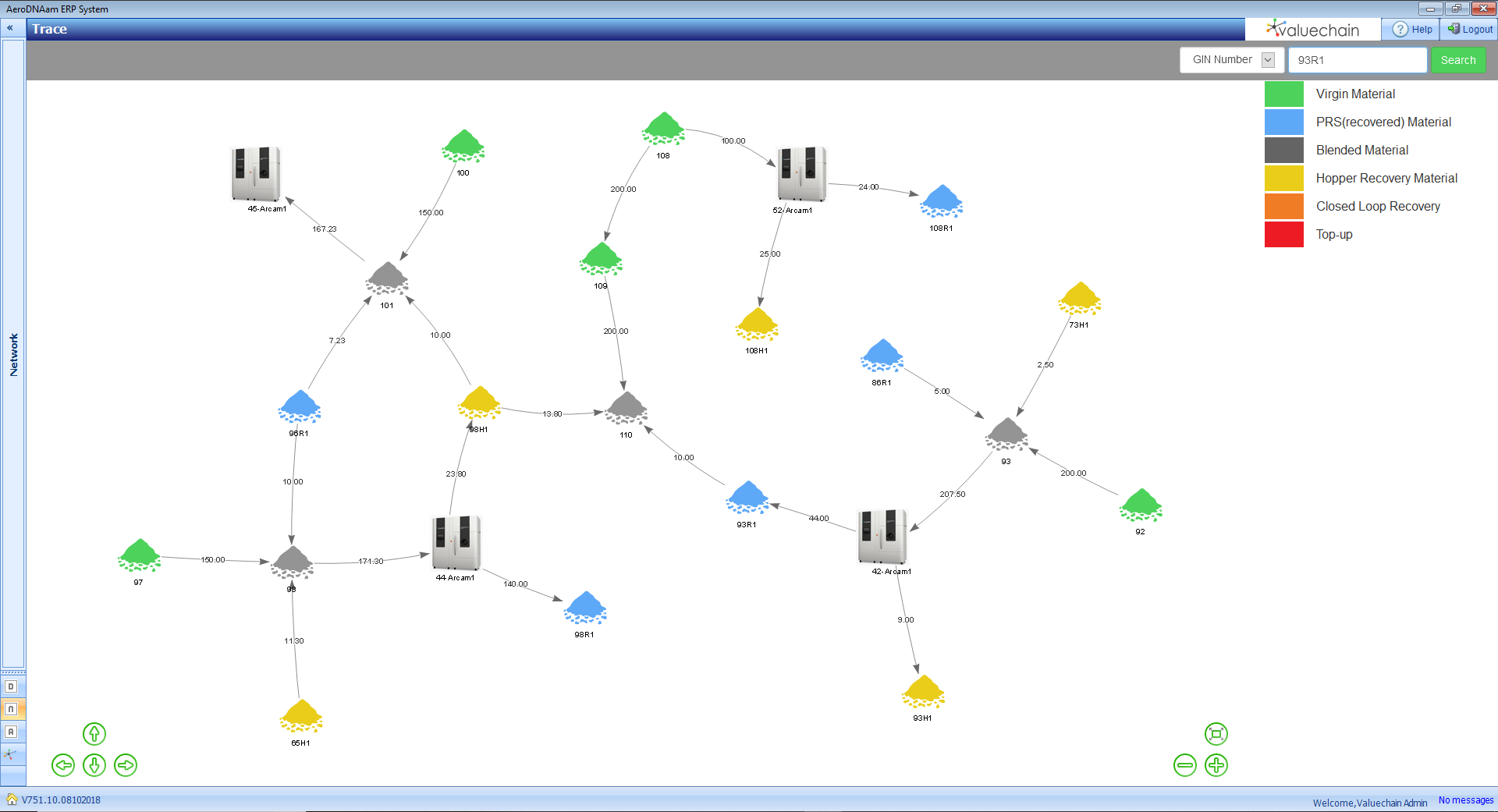
HiETA is also working on an Artificial Intelligence (AI) tool designed to characterize the powder feedstock for the 3D printing process in order to produce quality parts. The firm will use material data gained from the powder feedstock, including how its properties can change depending on its condition, for instance, whether it has been recycled, kept in storage, or blended with new batches.
“We will be gathering data from builds at HiETA and the MTC’s facilities, including our materials and inspection labs,” said Morrison. “HiETA will use that data to build an AI model which can help us control our powder better, and produce higher quality parts.”
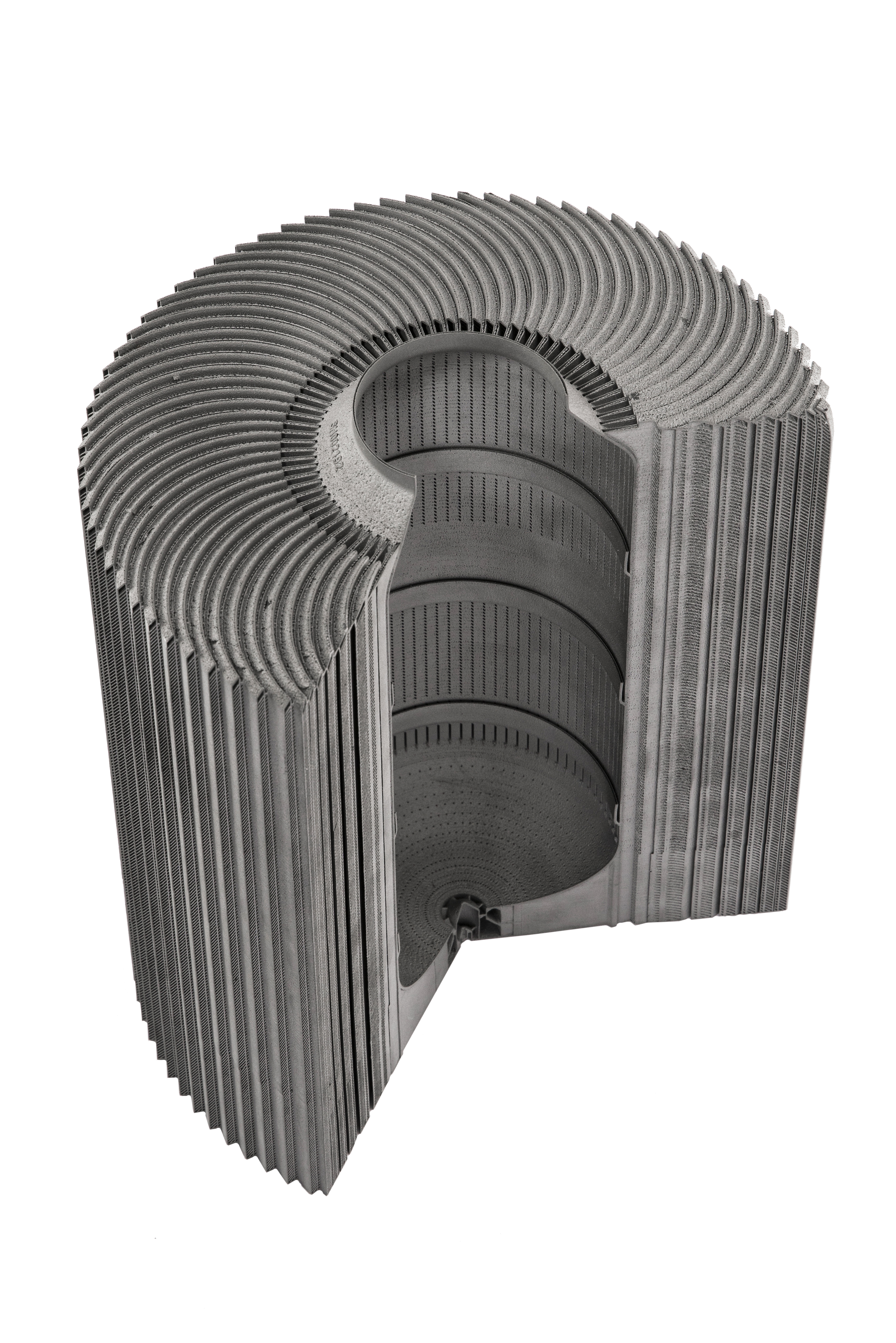
Photo by Adam Gasson / adamgasson.com
Industry 4.0, standardization, and data traceability
Equipped with expertise in Industry 4.0 and 3D printing software, during the project Valuechain will be extending its own software to enable an end-to-end digital thread throughout the additive manufacturing supply chain. The firm will be demonstrating best practice for the standardization and digitalization of 3D printing, and how supply chain members can benefit from this.
Arrowsmith, meanwhile, has a long history of supplying components to aerospace players such as Rolls Royce. Throughout the Daedalus project, the company will demonstrate how the move to additive manufacturing and a digital supply chain can be achieved while highlighting the standardization, data traceability, and quality advantages that this brings.
The MTC and NCAM will put their experience of the whole 3D printing process chain, and their work in digitizing additive manufacturing, into practice to support the other members of the consortium.
“Our role is to ensure that the solutions we develop on the project work for the entirety of the AM sector, and then to support them in adopting them through training courses, our knowledge hub, and our new learning facility,” continued Morrison. “Our digital teams will also be developing novel analytics which use new in-process data to predict defects in AM components.”
The MTC is also in charge of developing the project’s second AI thread, which will look at identifying internal defects in 3D printed components by building on its past work using AI vision systems. The MTC will take melt pool data from the 3D printing process – the thermal signature when the laser melts the powder – to detect defects in components as they are built.
“We hope this will lead to higher confidence in AM components; saving on expensive inspection processes like x-ray CT; and eventually even in-process corrections during the build,” Morrison adds.
Measuring Daedalus’ success
The MTC and NCAM already offer a variety of support and training for UK-based 3D printing manufacturers and will take the learnings from the Daedalus project to expand and further this provision. The organization hopes to offer increased support to companies in adopting 3D printing technology and improving their processes.
“For us at the MTC, our measure of success is the impact on the UK AM supply chain,” Morrison concludes. “The number of companies we support in adopting the technology; the number of people we can train and upskill; the number of jobs we can help create.”
Subscribe to the 3D Printing Industry newsletter for the latest news in additive manufacturing. You can also stay connected by following us on Twitter and liking us on Facebook.
Be sure to subscribe to the Another Dimension podcast on your chosen podcast player to make sure you never miss an episode.
Looking for a career in additive manufacturing? Visit 3D Printing Jobs for a selection of roles in the industry.
Featured image shows inside the National Centre for Additive Manufacturing. Photo via NCAM


