ESPRIT, the flagship software product from Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software developer DP Technology, has entered into a partnership with Almacam, a developer of CAD/CAM software for sheet metal working, cutting, and robotics, to create a complete programming offering for robot additive Direct Energy Deposition (DED).
The firms will combine their areas of expertise within advanced toolpath planning in both subtractive and additive areas and in robotics trajectory computation, to provide customers with an end-to-end program for robot additive DED.
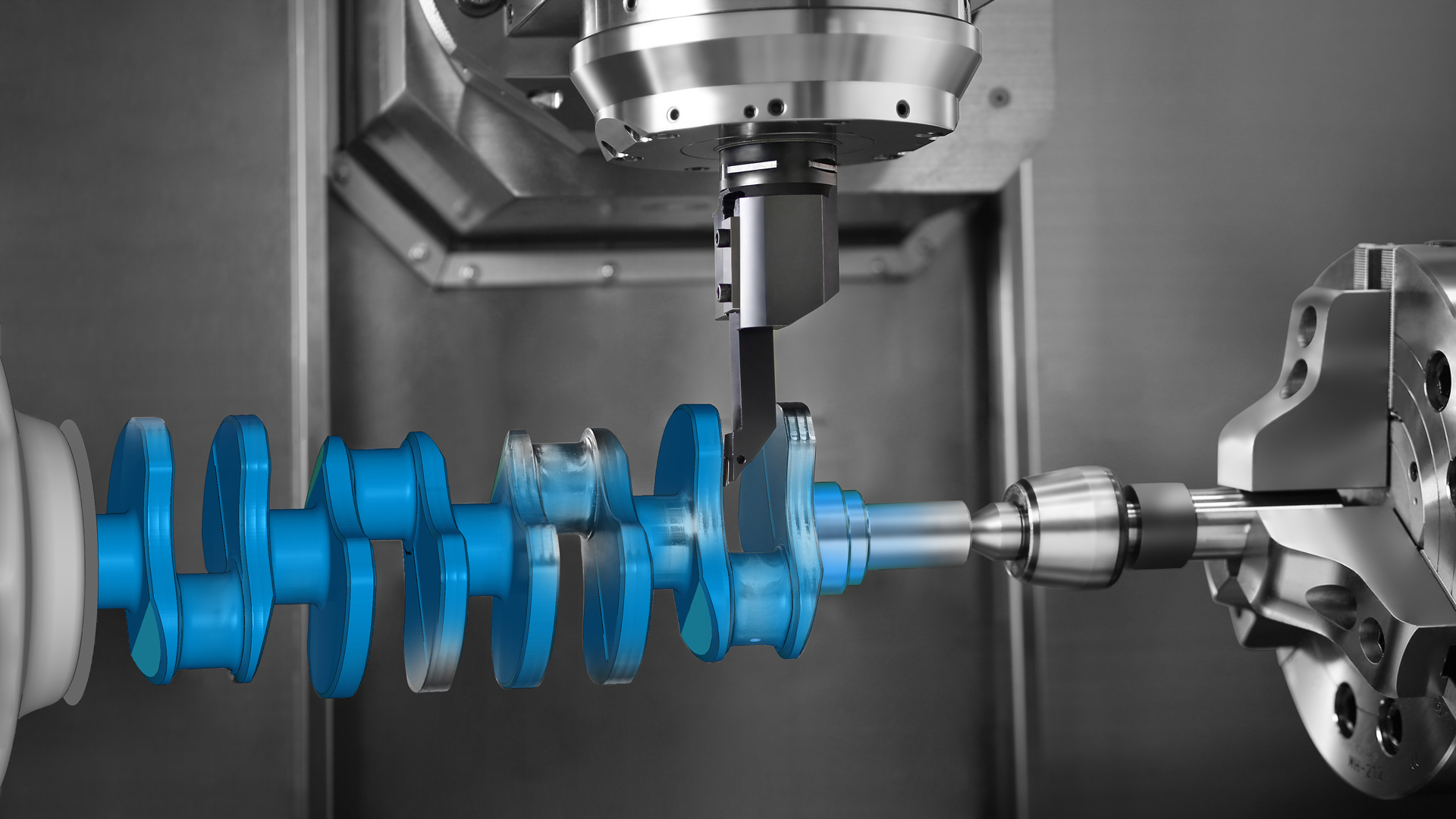

Additive DED
Additive DED involves the creation of parts by melting and fusing material as it is deposited, using multiple metal 3D printing technologies such as Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM). WAAM can provide notable reductions in cost and lead times in addition to increasing the efficiency of materials and improving component performance when utilized for robot additive DED.
Robotic DED machines cost significantly less than machine-tool based DED machines, which can cost up to millions of dollars. Companies can retrofit their existing programmable industrial robots for additive DED applications through determining the toolpath of the DED head and robotic arms, which is where the software offering from ESPRIT and Alma comes into play.
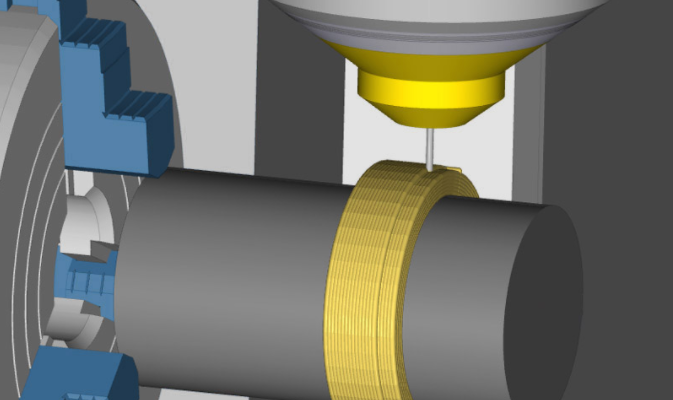
ESPRIT and Alma’s partnership
The technology partnership between ESPRIT and Alma will produce a complete workflow software equipping users with dedicated additive toolpath planning and programming. The software will also provide robot programming, simulation, and verification, alongside collision detection and code generation.
The collaboration will allow Alma to use ESPRIT’s additive DED cycles, 3x, 4x, and 5x, while enabling Esprit to support industrial robot brands such as Yaskawa, ABB, Fanuc, and Kuka. The firms have already collaborated with several customers and research institutions to validate the software for multiple applications, as well as carry out tests with various robot brands.
The workflow begins with the suite of additive operations available in ESPRIT CAM, where a part is programmed using ESPRIT’s automatic tool inclination DED cycle to produce toolpath trajectory calculations. A simulation of the cycle is then run in ESPRIT on a sample 5-axis DED machine to get an idea of the overall deposition and to verify the toolpath.
Once a suitable toolpath has been created, it can be applied to a robot cell through Almacam’s technology. Almacam reads the ESPRIT file and uses its own kinematic software to simulate and program the robot’s motion. This workflow then culminates in the manufacturing process through combining the toolpath from ESPRIT and the robot programming from Almacam.
ESPRIT and 3D printing
Earlier this year, DP Technology announced several software updates to the ESPRIT CAM system, the first of which included new features such as a balanced turning cycle, and enhancements to its existing probing and additive DED features.
Soon after, DP Technology released a new element of the ESPRIT software designed for Powder Bed Fusion (PBF). The program came as an add-on application for the computer-aided design (CAD) program SolidWorks, in order to increase the number of additive manufacturing processes it supports.
Most recently, DP Technology was acquired by the Hexagon AB technology consortium in a deal that will see the ESPRIT CAM system included in Hexagon’s Manufacturing Intelligence Division. It’s hoped that this global platform will boost ESPRIT’s presence in the marketplace.
Subscribe to the 3D Printing Industry newsletter for the latest news in additive manufacturing. You can also stay connected by following us on Twitter and liking us on Facebook.
Be sure to subscribe to the Another Dimension podcast on your chosen podcast player to make sure you never miss an episode.
Looking for a career in additive manufacturing? Visit 3D Printing Jobs for a selection of roles in the industry.
Featured image shows ESPRIT’s Additive DED software offers specialized toolpaths for additive processes. Image via ESPRIT.


