In this edition of Sliced, the 3D Printing Industry news digest, we cover the latest business developments, partnerships, and acquisitions across our industry.
Today’s edition features numerous 3D printer investments, software updates, new additive manufacturing partnerships, and a self-illuminating 3D printed guitar.
Read on for the most recent updates from the Royal Australian Navy, Nikola Corporation, 3DQue, Exactech, Accurate Brazing, Alloyed, Adidas, and more.
3D printer investments and order follow-ups from Volkswagen, Nikola Corporation, the Royal Australian Navy, and Voxeljet
Kicking off this week’s 3D printer updates is the news that automotive manufacturer Volkswagen has installed two PolyJet Technology-based J850 3D printers from 3D printer manufacturer Stratasys at its Pre-Series-Center. Volkswagen will use the new additions to 3D print a wide range of ultra-realistic prototypes for interior and exterior applications to aid in new vehicle design.
The J850 printers will enable Volkswagen to create complex full-color multi-material prototypes that mirror final production parts with up to 99% precision, allowing its design team to better test and improve part designs. Prototypes will be able to be printed in up to seven different materials comprising different rigidity, flexibility, opaqueness, and transparency properties in a single print, providing time and cost savings over traditional multi-step design processes.
Elsewhere, energy and transport component manufacturer Nikola Corporation has invested in a BigRep PRO additive manufacturing system from German large-format 3D printer manufacturer BigRep, with the aim of streamlining the production processes of its various electric vehicle systems and components. The BigRep PRO will assist Nikola in the 3D printing of highly-precise assembly, weld, and Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM) inspection fixtures, and will also produce test components for sizing checks on the company’s battery-electric and hydrogen fuel-cell electric vehicles. The BigRep PRO will also manufacture some end-use parts.
“We selected the BigRep PRO for its large-format build volume, third-party filament compatibility, and state-of-the-art Bosch-Rexroth CNC control systems,” said Riley Gillman, Technical Operations Manager of Nikola Corporation. “The first prints that we ran lasted 17 days. Since then, we have been pretty much running the PRO non-stop to help us print parts and components using its large capacity of printing, high resolution and accuracy throughout the entire process.”
Meanwhile, the Royal Australian Navy has become the latest Australian Defence service to invest in 3D printing technology following the installation of a large-format WarpSPEE3D metal 3D printer at HMAS Coonawarra Navy Port. Thanks to a $1.5 million investment from the Australian Government, an 18-month pilot trial of the WarpSPEE3D will seek to streamline the maintenance of patrol vessels and increase part availability for the Navy, enabling it to design and print required parts when needed while on base and at sea.
SPEE3D recently completed a series of successful field trials of the WarpSPEE3D printer with the Australian Army. CEO Byron Kennedy said: “We are excited to be working with The Royal Australian Navy on this program. Having the capability to produce high-quality metal parts on-demand, in the field or at sea will be ground-breaking for the Australian Defence Force.”
German 3D printer manufacturer voxeljet has received a follow-up order for three additional units of its high-speed VJET X 3D printer, as part of a frame contract with a leading German car maker. The unnamed OEM now has a total of five VJET X units which, voxeljet says, confirms its 3D printers are making cost-effective high-volume additive serial production a reality.
With printing speeds 10 times faster than previous models, the VJET X is integrated into fully automated post-processing operations. The printer uses a zero-emission inorganic binder system during core printing, storage, and when using sand cores in the casting process.
“With this order we reached a significant milestone in our mission to bring 3D printing into high-volume industrial production,” said Ingo Ederer, founder and CEO of voxeljet. “Together with our partners, we can today offer a solution for the mass production of complex sand cores for light metal parts at, what we believe to be, a fraction of the costs as compared to other players in the additive manufacturing industry.”

Xometry makes Deloitte’s Technology Fast 500
Global manufacturing marketplace Xometry has been ranked 126th on accounting organization Deloitte’s Technology Fast 500 list in North America, as a result of its 949 percent growth between 2016-19. The Fast 500 list is an annual ranking of the fastest-growing North American companies across a range of sectors, including technology, media, telecommunications, fintech, life sciences, and energy tech sectors.
“Xometry continues to grow quickly, even in the midst of Covid-related supply chain disruptions,” commented Randy Altschuler, Xometry CEO. “I am proud of our team’s incredible work and would like to thank Deloitte for recognizing us on this year’s Fast 500 list. We are honored to be included along with many companies that, like us, are transforming their respective industries.”
In September, Xometry announced it had gained $75 million in equity funding, taking its total raised since 2013 to $193 million.

Software updates from Renishaw and 3DQue
Global engineering technologies firm Renishaw has released the latest version of its CARTO software for calibration products, CARTO 4.2. The latest update employs dynamic data fit (DDF) functionality to facilitate the capture and analysis of data from linear axes of any length via Renishaw’s XM-60 multi-axis calibrator.
The software’s DDF addition enables XM-60 users to capture straightness measurements dynamically, after which the data is recalculated in CARTO capture to reduce outlying data-points to lessen exposure to environmental interference. Another new addition included within CARTO 2.4 is the Heidenhain linear compensation option, which allows users to quickly and easily apply pitch error compensation to Heidenhain machine tool controls.
Vancouver-based 3D printing start-up 3DQue has released a plug-and-play kit for its automated 3D print manager, Quinly. The PI Kit provides all the cables and hardware needed to install a Raspberry Pi 4 on any Ender 3 series printer, enabling users to access their Quinly software via a WiFi connection, from anywhere.
“Ender 3 printers don’t come with the computing power needed to run automation software and connect wirelessly,” said Mateo Pekic, co-founder and chief of innovations at 3DQue. “While many of our customers have Raspberry Pi 4s, those who don’t have one want an easy-to-use solution with our Quinly software already installed. The Pi Kit for Quinly gives them that.”

Relativity Space closes $500m series D financing round
Californian 3D printed rocket manufacturer Relativity Space has closed a $500 million Series D equity funding round led by Tiger Global Management, and with participation from new investors Fidelity, Baillie Gifford, ICONIQ Capital, General Catalyst, XN, Senator Investment Group, and Elad Gil. Looking ahead to what the firm says will be “humanity’s multiplanetary future”, the Series D funding will enable Relativity to accelerate its ongoing initiatives, such as its factory of the future, launch vehicle development, and 3D printing technologies.
“This past year drove change in every industry, including aerospace,” said Tim Ellis, Relativity’s co-founder and CEO. “Throughout 2020, Relativity achieved unprecedented growth, attracted top talent, and stepped up to deliver results we could have only imagined when we started the company less than five years ago.”
The firm is due to launch its first Terran 1 rocket to orbit next year, which is currently being built at Relativity’s new HQ in Long Beach, California.
New 3D printing partnerships from GE Additive and Exactech
Industrial 3D printer manufacturer GE Additive has signed a consultancy agreement with golf equipment manufacturer Callaway Golf to redesign the company’s Odyssey R-Ball putter. After reaching the design limitations of traditional manufacturing techniques the firm was using, Callaway sought to explore how efficiently it could change the acoustics of the putter through additive manufacturing.
Through the partnership, GE Additive and Callaway will investigate ways of improving Callaway products through additive manufacturing, and will use GE’s expertise in the build constraints of 3D printing to produce optimized end-use parts with higher performance. From GE’s perspective, the collaboration will provide insight into other industries from which it can take learnings and feed this back into improving its machines to better serve customer needs.
Meanwhile, medical device manufacturing firm Exactech has added orthopedic manufacturer Bodycad’s Reflex Uni knee replacement to its Truliant Knee System, which received 510(k) clearance in March. Bodycad developed the Truliant Reflex Uni, a personalized unicompartmental knee implant, using its proprietary software algorithm and fully integrated 3D printing production system, the aim of which is to optimize customized, patient-specific anatomy replacements. Exactech will distribute the Truliant Reflex Uni within the U.S.
“Innovation in unicompartmental knee implants has been stagnant for years,” said John McDaniel, Exactech’s senior vice president, Large Joints. “We intentionally delayed offering a partial knee until we had something that could address the shortcomings of existing designs. With Truliant Reflex Uni, surgeons have the option to change implant design and placement to meet the needs of each patient.
“We’re excited about this personalized solution and its potential to maximize bone coverage, achieve proper alignment, and optimize joint function.”
Facility installations from Accurate Brazing and Alloyed
Heat treatment specialist Accurate Brazing will add a second Hot Isostatic Press unit to its Greenville facility in South Carolina in February 2021, in order to continue meeting the needs of its aerospace customers. The QIH 122 M URC press is produced by high pressure technology firm Quintus Technologies, and is equipped with Quintus’ proprietary uniform rapid cooling (URC) feature combining HIP and heat treatment in a single process, called High Pressure Heat Treatment (HPHT). HPHT streamlines material densification and heat treatment processes while also allowing processed components to cool uniformly to minimize thermal distortion.
“The Quintus technology allows us to shorten lead times, improve product metallurgy, and eliminate some additional outside operations, which is very attractive to our customers,” said Steven Francis, Accurate Brazing president. The press is expected to be operational in Q2 2021.
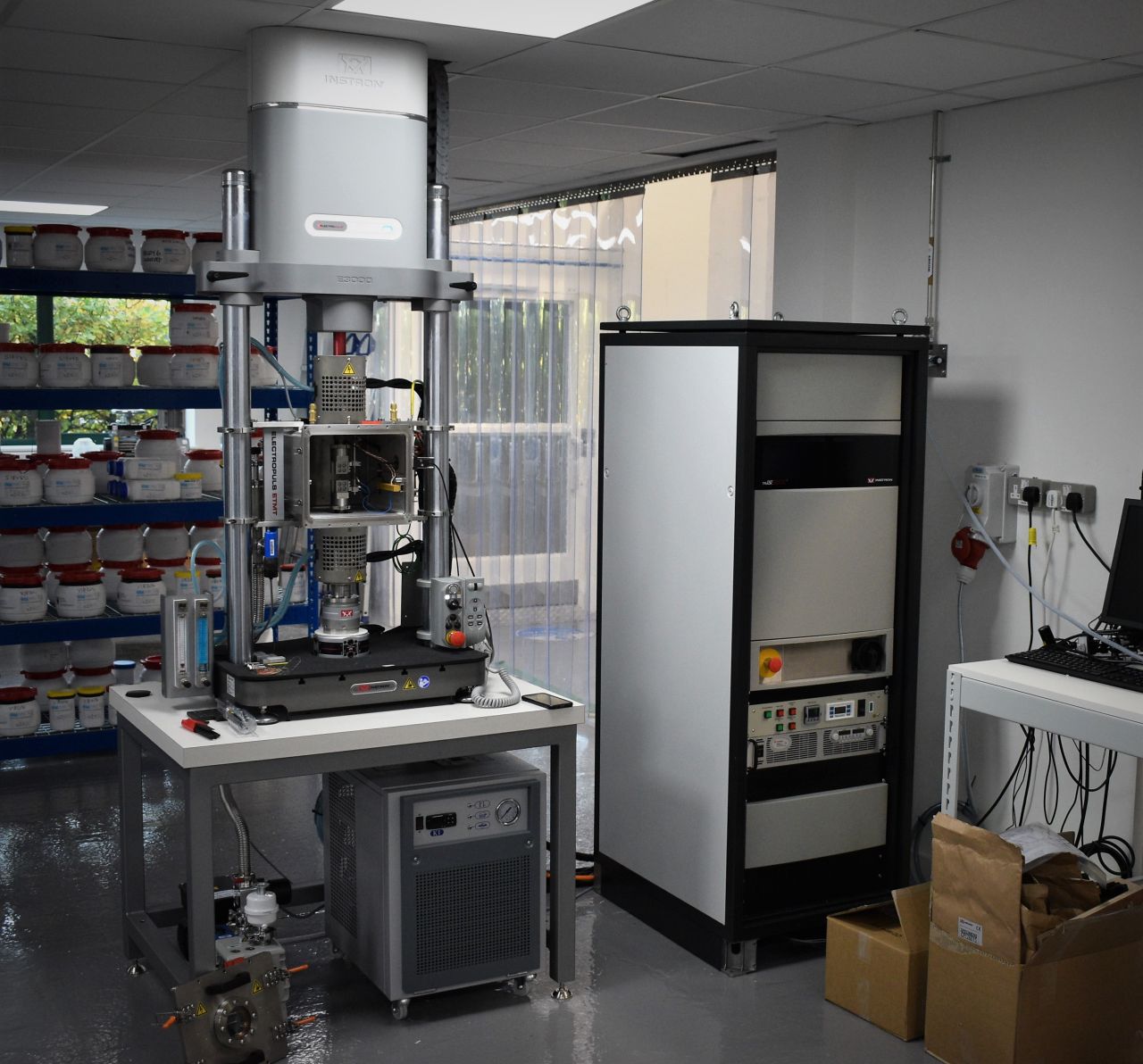
On the other side of the Atlantic, metal alloy specialist Alloyed has invested $300,000 in an Electro-Thermal Mechanical Testing (ETMT) machine for its 1,000 meter square laboratory in Oxford, in a bid to become a one-stop-shop for metal testing. In light of the investment, Alloyed becomes one of only a handful of private companies to have this technology in-house.
The ETMT machine can perform tensile and compression tests, stress-rupture tests, and fatigue tests, under a variety of conditions such as in air, vacuum, or foreign gases such as Argon. Previously, these tests would have had to be outsourced to numerous testing companies with access to these technologies.
“At Alloyed, we have equipped the ETMT with a state-of-the-art digital image correlation (DIC) system, which allows us to optically measure strain on the sample during testing,” said Gael Guetard, Alloyed’s rapid alloy research center director. “The machine is well-suited for miniature test specimens, which allows us to obtain site-specific mechanical properties from large parts such as forgings. We have also found it very valuable in measuring the properties of finely additively manufactured structures like lattices or thin walls.”
Alloyed recently formalized its legal name after concluding a merger between Betatype and OxMet Technologies.

Adidas tips hat to NASA with ‘Halo Silver’ Ultra4D sneaker
Adidas has released a new NASA-inspired ‘Halo Silver’ colorway for its 3D printed Ultra4D sneaker, featuring a blue Artemis insignia on the tongue and the classic NASA logo on the heel. Adidas has previously announced a partnership with the International SpaceStation (ISS) to test its products in space, which is likely the reason for the inspired design.
Adidas’ first Futurecraft running shoe, the 4D, was created by Carbon utilizing its Digital Light Synthesis (DLS) 3D printing technology. In January 2018, the first fully-formed pair of 4D sneakers became available for purchase. Since then, Adidas has gone on to collaborate with fashion brand Stella McCartney to develop its AlphaEdge 4D silhouette trainers, and most recently released its Futurecraft ‘STRUNG’ running shoe.

Lighting up the stage with 3D printing
To round off this week’s news, we will leave you with this 3D printed guitar that lights up when played, designed and built by 3D printing enthusiast Josh Henderson. Not only did Henderson 3D print the guitar, but he also built the 3D printer the guitar was produced on. Over a total of 60 hours, the guitar body was printed in white ABS to allow LEDs in the back of the guitar the shine through.
For the next stage of his project, Henderson will seek to light up the neck of the guitar in the same way the body does, add a digital to analog converter (DAC) to the electronics board, and, of course, add more LED lighting modes. Rock and Roll!
Subscribe to the 3D Printing Industry newsletter for the latest news in additive manufacturing. You can also stay connected by following us on Twitter and liking us on Facebook.
Be sure to subscribe to the Another Dimension podcast on your chosen podcast player to make sure you never miss an episode.
Looking for a career in additive manufacturing? Visit 3D Printing Jobs for a selection of roles in the industry.
Featured image shows Joshua Henderson’s 3D printed guitar with the SLICED logo.


